reshape
- paddle. reshape ( x: Tensor, shape: ShapeLike, name: str | None = None ) Tensor [source]
-
Changes the shape of
xwithout changing its data.Note that the output Tensor will share data with origin Tensor and doesn’t have a Tensor copy in
dygraphmode. If you want to use the Tensor copy version, please use Tensor.clone likereshape_clone_x = x.reshape([-1]).clone().Some tricks exist when specifying the target shape.
-
-1 means the value of this dimension is inferred from the total element number of x and remaining dimensions. Thus one and only one dimension can be set -1.
-
0 means the actual dimension value is going to be copied from the corresponding dimension of x. The index of 0s in shape can not exceed the dimension of x.
Here are some examples to explain it.
-
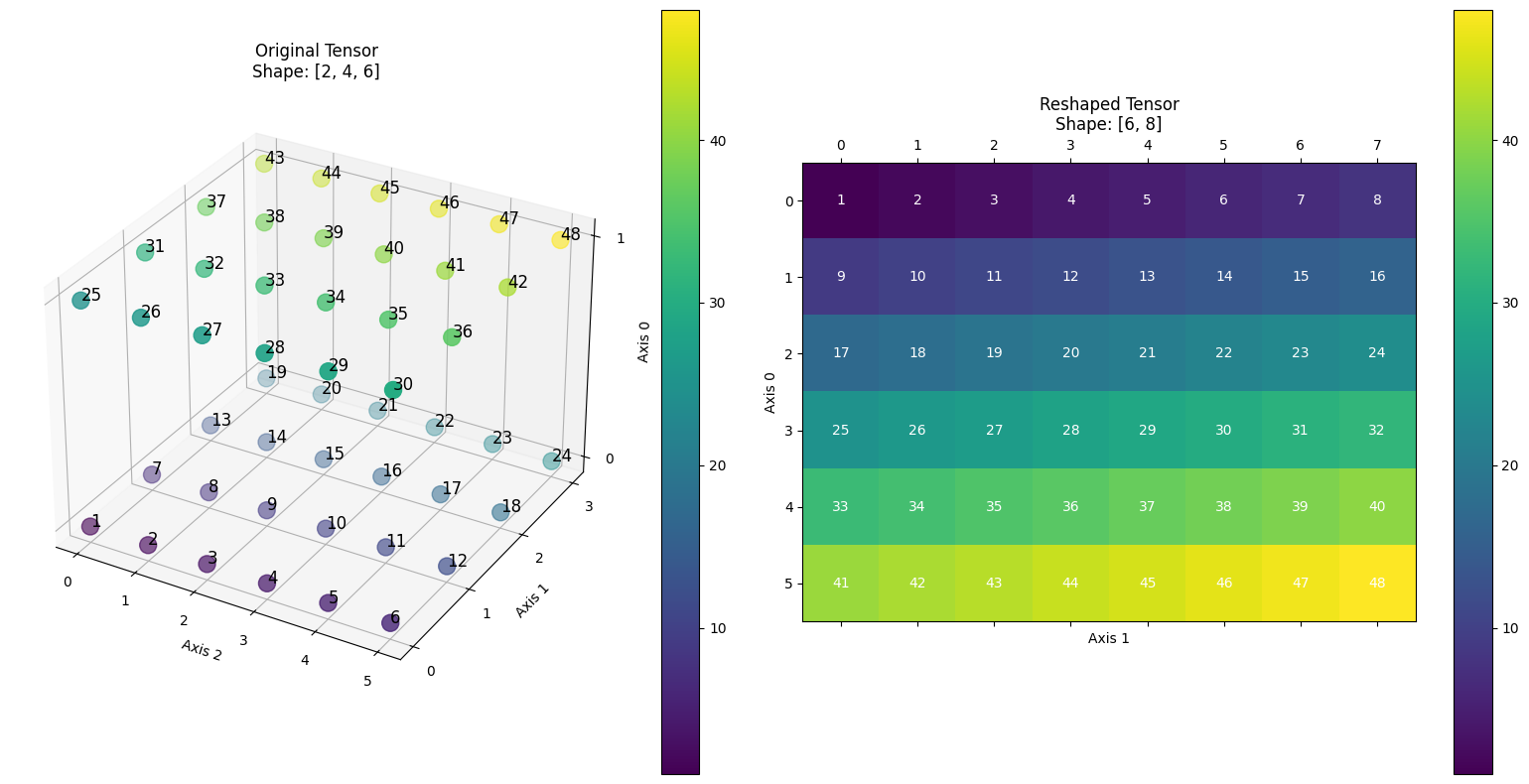
Given a 3-D tensor x with a shape [2, 4, 6], and the target shape is [6, 8], the reshape operator will transform x into a 2-D tensor with shape [6, 8] and leaving x’s data unchanged.
-
Given a 3-D tensor x with a shape [2, 4, 6], and the target shape specified is [2, 3, -1, 2], the reshape operator will transform x into a 4-D tensor with shape [2, 3, 4, 2] and leaving x’s data unchanged. In this case, one dimension of the target shape is set to -1, the value of this dimension is inferred from the total element number of x and remaining dimensions.
-
Given a 3-D tensor x with a shape [2, 4, 6], and the target shape is [-1, 0, 3, 2], the reshape operator will transform x into a 4-D tensor with shape [2, 4, 3, 2] and leaving x’s data unchanged. In this case, besides -1, 0 means the actual dimension value is going to be copied from the corresponding dimension of x.
The following figure illustrates the first example – a 3D tensor of shape [2, 4, 6] is transformed into a 2D tensor of shape [6, 8], during which the order and values of the elements in the tensor remain unchanged. The elements in the two subdiagrams correspond to each other, clearly demonstrating how the reshape API works.
- Parameters
-
x (Tensor) – An N-D Tensor. The data type is
float16,float32,float64,int16,int32,int64,int8,uint8,complex64,complex128,bfloat16orbool.shape (list|tuple|Tensor) – Define the target shape. At most one dimension of the target shape can be -1. The data type is
int32. Ifshapeis a list or tuple, each element of it should be integer or Tensor with shape []. Ifshapeis a Tensor, it should be an 1-D Tensor .name (str, optional) – Name for the operation (optional, default is None). For more information, please refer to Name.
- Returns
-
Tensor, A reshaped Tensor with the same data type as
x.
Examples
>>> import paddle >>> x = paddle.rand([2, 4, 6], dtype="float32") >>> positive_four = paddle.full([1], 4, "int32") >>> out = paddle.reshape(x, [-1, 0, 3, 2]) >>> print(out.shape) [2, 4, 3, 2] >>> out = paddle.reshape(x, shape=[positive_four, 12]) >>> print(out.shape) [4, 12] >>> shape_tensor = paddle.to_tensor([8, 6], dtype=paddle.int32) >>> out = paddle.reshape(x, shape=shape_tensor) >>> print(out.shape) [8, 6] >>> # out shares data with x in dygraph mode >>> x[0, 0, 0] = 10. >>> print(out[0, 0]) Tensor(shape=[], dtype=float32, place=Place(cpu), stop_gradient=True, 10.) -

