hstack
- paddle. hstack ( x: Sequence[Tensor], name: str | None = None ) Tensor [source]
-
Stacks all the input tensors
xalong horizontal axis. All tensors must be of the same dtype.The image below illustrates how
hstackworks.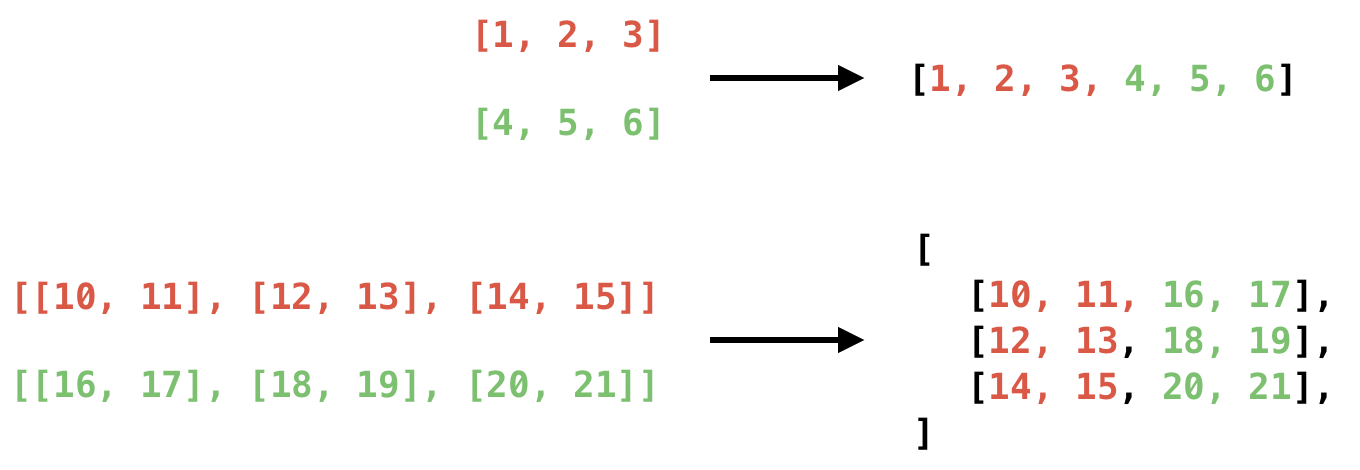
- Parameters
-
x (list[Tensor]|tuple[Tensor]) – Input
xcan be alistortupleof tensors, the Tensors inxmust be of the same shape and dtype. Supported data types:float16,float32,float64,int8,int32,int64orbfloat16.name (str|None, optional) – Name for the operation (optional, default is None). For more information, please refer to Name.
- Returns
-
Tensor, The stacked tensor with same data type as input.
Examples
>>> import paddle >>> # hstack with 0-D tensors >>> x1 = paddle.to_tensor(1.0) >>> x2 = paddle.to_tensor(2.0) >>> out = paddle.hstack((x1, x2)) >>> print(out) Tensor(shape=[2], dtype=float32, place=Place(cpu), stop_gradient=True, [1., 2.]) >>> # hstack with 1-D tensors >>> x1 = paddle.to_tensor([1.0, 2.0]) >>> x2 = paddle.to_tensor([3.0, 4.0, 5.0]) >>> out = paddle.hstack((x1, x2)) >>> print(out) Tensor(shape=[5], dtype=float32, place=Place(cpu), stop_gradient=True, [1., 2., 3., 4., 5.]) >>> # hstack mix with 0-D & 1-D tensors >>> x1 = paddle.to_tensor(1.0) >>> x2 = paddle.to_tensor([3.0, 4.0, 5.0]) >>> out = paddle.hstack((x1, x2)) >>> print(out) Tensor(shape=[4], dtype=float32, place=Place(cpu), stop_gradient=True, [1., 3., 4., 5.]) >>> # hstack with 2-D tensors >>> x1 = paddle.to_tensor([[1.0, 2.0]]) >>> x2 = paddle.to_tensor([[3.0, 4.0, 5.0]]) >>> out = paddle.hstack((x1, x2)) >>> print(out) Tensor(shape=[1, 5], dtype=float32, place=Place(cpu), stop_gradient=True, [[1., 2., 3., 4., 5.]])

