index_fill
- paddle. index_fill ( x: Tensor, index: Tensor, axis: int, value: float, name: str | None = None ) [source]
-
Fill the elements of the input tensor with value by the specific axis and index.
As shown below, a
[3, 3]2D tensor is updated via the index_fill operation. Withaxis=0,index=[0, 2]andvalue=-1, the 1st and 3rd row elements become-1. The resulting tensor, still [3, 3], has updated values.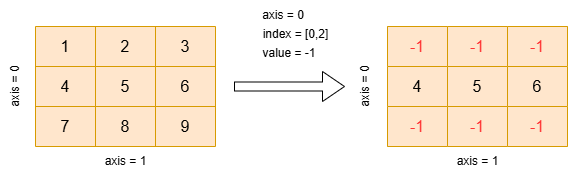
- Parameters
-
x (Tensor) – The Destination Tensor. Supported data types are int32, int64, float16, float32, float64.
index (Tensor) – The 1-D Tensor containing the indices to index. The data type of
indexmust be int32 or int64.axis (int) – The dimension along which to index.
value (int|float) – The tensor used to fill with.
name (str|None, optional) – For details, please refer to Name. Generally, no setting is required. Default: None.
- Returns
-
Tensor, same dimension and dtype with x.
Examples
>>> import paddle >>> input_tensor = paddle.to_tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]], dtype='int64') >>> index = paddle.to_tensor([0, 2], dtype="int32") >>> value = -1 >>> res = paddle.index_fill(input_tensor, index, 0, value) >>> print(input_tensor) Tensor(shape=[3, 3], dtype=int64, place=Place(gpu:0), stop_gradient=True, [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]) >>> print(res) Tensor(shape=[3, 3], dtype=int64, place=Place(gpu:0), stop_gradient=True, [[-1, -1, -1], [ 4, 5, 6], [-1, -1, -1]])

