expand
- paddle. expand ( x: Tensor, shape: ShapeLike, name: str | None = None ) Tensor [source]
-
Expand the input tensor to a given shape.
Both the number of dimensions of
xand the number of elements inshapeshould be less than or equal to 6. And the number of dimensions ofxshould be less than the number of elements inshape. The dimension to expand must have a value 0.The image illustrates a typical case of the expand operation. The Original Tensor is a 1D tensor with shape
[3]and values [1, 2, 3]. Using thepaddle.expandmethod with the parametershape = [2, 3], it is broadcasted and expanded into a 2D tensor with shape[2, 3]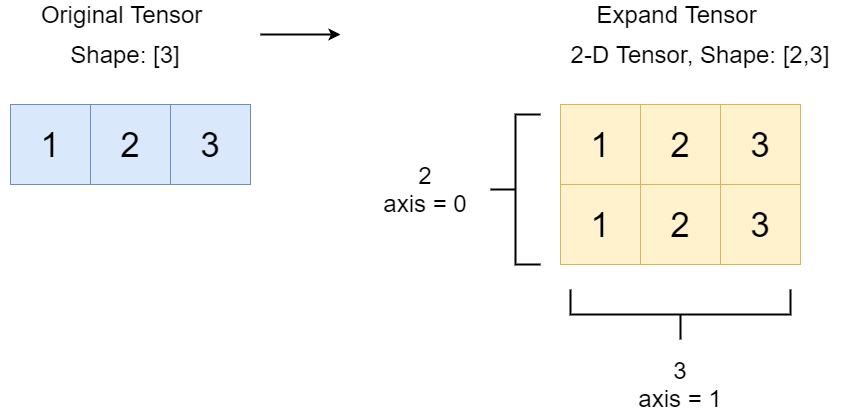
- Parameters
-
x (Tensor) – The input Tensor, its data type is bool, float16, float32, float64, int32, int64, uint8, uint16, complex64 or complex128.
shape (list|tuple|Tensor) – The result shape after expanding. The data type is int32. If shape is a list or tuple, all its elements should be integers or 0-D or 1-D Tensors with the data type int32. If shape is a Tensor, it should be an 1-D Tensor with the data type int32. The value -1 in shape means keeping the corresponding dimension unchanged.
name (str|None, optional) – The default value is None. Normally there is no need for user to set this property. For more information, please refer to Name .
- Returns
-
N-D Tensor, A Tensor with the given shape. The data type is the same as
x.
Examples
>>> import paddle >>> data = paddle.to_tensor([1, 2, 3], dtype='int32') >>> out = paddle.expand(data, shape=[2, 3]) >>> print(out) Tensor(shape=[2, 3], dtype=int32, place=Place(cpu), stop_gradient=True, [[1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3]])

