hsplit
- paddle. hsplit ( x: Tensor, num_or_indices: int | Sequence[int], name: str | None = None ) list[Tensor] [source]
-
hsplitFull name Horizontal Split, splits the input Tensor into multiple sub-Tensors along the horizontal axis, in the following two cases:When the dimension of x is equal to 1, it is equivalent to
paddle.tensor_splitwithaxis=0;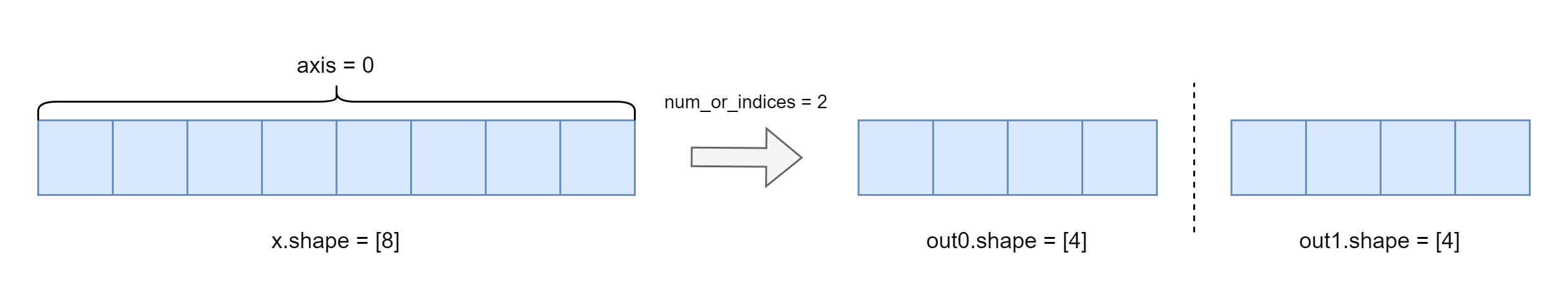
when the dimension of x is greater than 1, it is equivalent to
paddle.tensor_splitwithaxis=1.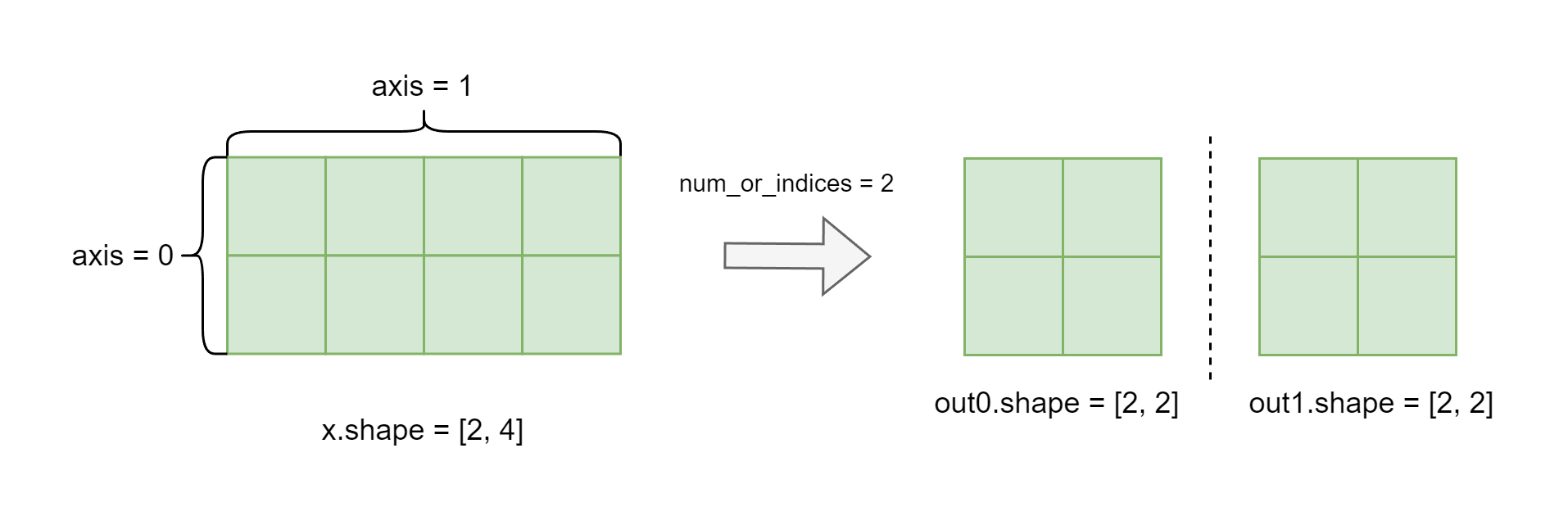
- Parameters
-
x (Tensor) – A Tensor whose dimension must be greater than 0. The data type is bool, bfloat16, float16, float32, float64, uint8, int32 or int64.
num_or_indices (int|list|tuple) – If
num_or_indicesis an intn,xis split intonsections. Ifnum_or_indicesis a list or tuple of integer indices,xis split at each of the indices.name (str|None, optional) – The default value is None. Normally there is no need for user to set this property. For more information, please refer to Name .
- Returns
-
list[Tensor], The list of segmented Tensors.
Examples
>>> import paddle >>> # x is a Tensor of shape [8] >>> x = paddle.rand([8]) >>> out0, out1 = paddle.hsplit(x, num_or_indices=2) >>> print(out0.shape) [4] >>> print(out1.shape) [4] >>> # x is a Tensor of shape [7, 8] >>> x = paddle.rand([7, 8]) >>> out0, out1 = paddle.hsplit(x, num_or_indices=2) >>> print(out0.shape) [7, 4] >>> print(out1.shape) [7, 4] >>> out0, out1, out2 = paddle.hsplit(x, num_or_indices=[1, 4]) >>> print(out0.shape) [7, 1] >>> print(out1.shape) [7, 3] >>> print(out2.shape) [7, 4]

