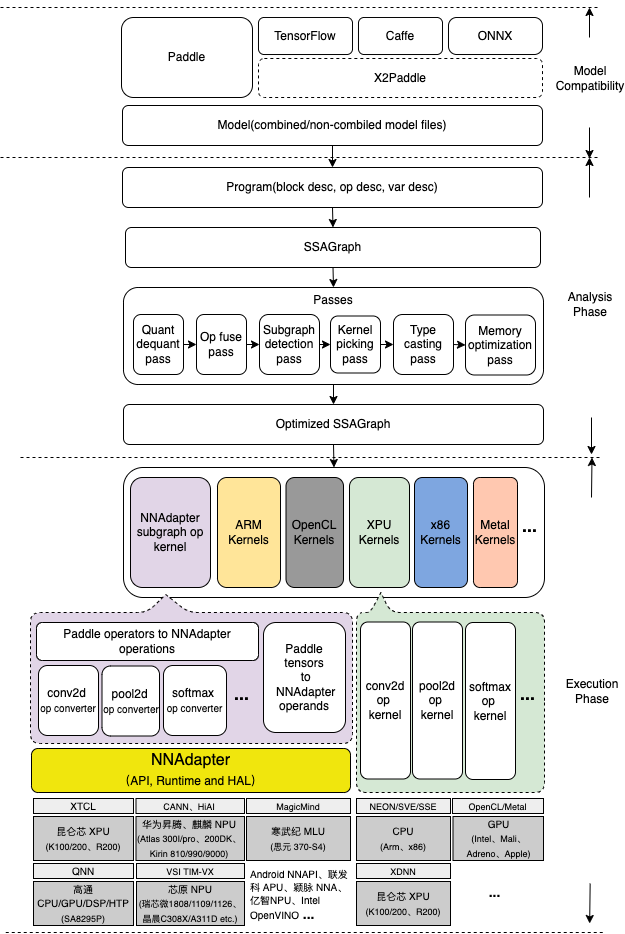
NNAdapter:飞桨推理 AI 硬件统一适配框架¶
背景¶
在新增硬件章节中曾提到 Paddle Lite 的硬件适配主要分为算子和子图两种方式,特别是 AI 硬件,近两年来我们基于子图方式完成了华为麒麟 NPU 、瑞芯微 NPU 、联发科 APU 、颖脉 NNA 、寒武纪 MLU 和比特大陆 NPU 在 Paddle Lite 上的适配。但在与硬件厂商合作过程中,逐渐发现了该方案的不足之处,主要涉及以下两大方面:
适配门槛高、周期长
要求硬件厂商对 Paddle Lite 有较深的了解,涵盖框架运行机制、硬件接入方案、编译系统等方面。
获取 Paddle 模型、算子定义、量化实现方式等信息所花费的沟通成本过高。
适配代码与框架过度耦合,且存在重复开发、代码维护成本过高
适配一个新的硬件并跑通一个分类模型,总的新增/修改文件数共 48 ,其中推理框架的文件修改数高达 25 。
Paddle 算子转硬件算子存在重复开发,且一旦 Paddle 算子发生升级,就需要对已支持的所有硬件的相关代码进行适配,维护成本过高。
量化方式( Paddle 仅支持对称量化,而大部分 SoC 类 NPU 支持非对称量化)、数据布局(例如联发科 APU 仅支持 NHWC ,而 Paddle 大部分模型为 NCHW 格式)的转换等模块存在重复实现,不利于各硬件间的共享达到缩减适配周期、降低维护成本的目的。
简介¶
NNAdapter 是什么?
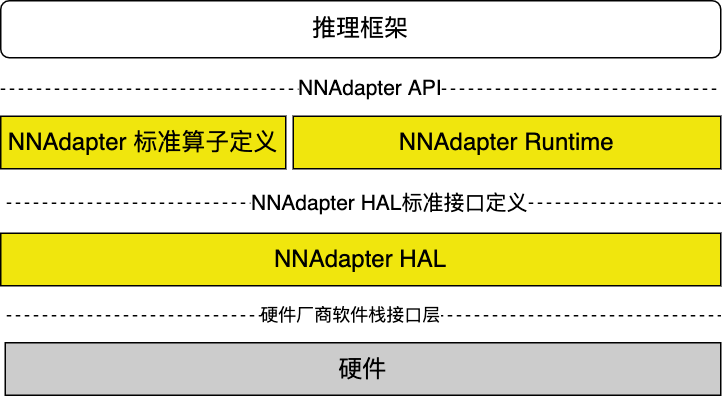
由一系列 C 接口组成的、支撑各种深度学习框架在各种硬件(特别是 AI ASIC 芯片)完成高效推理的通用接口,它是建立深度学习推理框架和硬件的桥梁,包含 API 、Runtime 、HAL 三层,以及模型中间表示层的标准算子定义。
NNAdapter 的目的是什么?
降低接入门槛,不要求硬件厂商深入了解 Paddle Lite 框架,只需了解 NNAdapter 的标准算子定义、HAL层标准接口定义、 Runtime 与 HAL 层的调用关系即可。
减少适配工作量,缩短适配周期,只需完成硬件的 HAL 层库的开发即可。
与推理框架解耦,降低维护成本。
NNAdapter 做了哪些工作?
标准化向上(推理框架)的接口,包括设备管理、模型组网、生成和执行的一系列 C 接口。
标准化算子定义,提供稳定的、文档丰富的中间表示层的算子定义(主要参考 ONNX 、 Paddle 、 PyTorch 和 TensorFlow 的算子),方便硬件厂商快速完成算子映射/转换。
标准化向下(硬件)抽象层( HAL )的接口定义,实现对硬件设备的抽象和封装(屏蔽硬件细节),为 NNAdapter 在不同硬件设备提供统一的访问接口。
功能模块¶
NNAdapter API¶
类似于 Google 的 Android NNAPI 、NVIDIA 的 TensorRT 、 Intel 的 OpenVINO ,为了实现与推理框架的完全解耦,方便适配不同的推理框架,需要提供包含设备管理、统一设备上下文、模型组网、编译和执行等在内的、完备的、稳定的 API (参考 NNAPI 命名规则),实现从设备初始化、模型组网、设备代码生成、执行、获取结果一系列完整的模型推理链条的打通。
设备管理
查询设备基本信息(名称、厂商、加速卡类型、 HAL 版本),完成设备的初始化等。
NNAdapterDevice_acquire 、 NNAdapterDevice_release 、 NNAdapterDevice_getName 、 NNAdapterDevice_getVendor 、 NNAdapterDevice_getType 、 NNAdapterDevice_getVersion
统一设备上下文
建立多种设备统一的设备上下文,可配置设备、编译、运行等基本参数,用于后续的模型编译和执行。
NNAdapterContext_create 、 NNAdapterContext_destroy
模型组网
创建与设备无关的、统一的模型的中间表达,实现推理框架模型的表达向NNAdapter模型表达的转换,具体是向模型实例中添加操作符实例(神经网络模型的算子)、操作数实例(神经网络模型的张量)进行模型组网。
NNAdapterModel_create 、 NNAdapterModel_destroy 、 NNAdapterModel_finish 、 NNAdapterModel_addOperand 、 NNAdapterModel_setOperandValue 、 NNAdapterModel_getOperandType 、 NNAdapterModel_addOperation 、 NNAdapterModel_identifyInputsAndOutputs
模型编译
创建模型编译配置,将模型编译生成适用于目标设备的程序代码,编译过程是通过设备HAL层库调用厂商 SDK 完成的。
NNAdapterCompilation_create 、 NNAdapterCompilation_destroy 、 NNAdapterCompilation_finish 、 NNAdapterCompilation_queryInputsAndOutputs
模型执行
基于已编译好的设备程序代码,创建执行计划并设置输入、输出,运行后将结果返回给推理框架。
NNAdapterExecution_create 、 NNAdapterExecution_destroy 、 NNAdapterExecution_setInput 、 NNAdapterExecution_setOutput 、 NNAdapterExecution_compute
注意:每个 API 的详细说明可以参考『附录』中的『 NNAdapter API 详细说明』章节。
NNAdapter 标准算子¶
为了建立独立与推理框架的、设备无关的、统一的模型的中间表达,要求对 NNAdapter 模型中算子进行标准化,涉及数学、图像、神经网络等类别。
例如:
typedef enum { ... /** * Performs element-wise binary addition(with Numpy-style broadcasting * https://numpy.org/doc/stable/user/basics.broadcasting.html). * * Inputs: * * 0: input0, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, * NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor. * * 1: input1, a tensor with the same type as input0. * * 2: fuse_code, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, specifies the activation to the * result, must be one of NNAdapterFuseCode values. * * Outputs: * * 0: output, the result with the same type as two inputs. * * Available since version 1. */ NNADAPTER_ADD, ... } NNAdapterOperationCode;
上述代码摘选自 nnadapter.h ,描述了
逐元素相加操作符 ADD的基本功能、输入操作数、输出操作数和适用的 NNAdapter 版本,值得注意的是:操作符的输入、输出操作数列表中的每一个操作数需要严格按照定义的顺序排列。注意:每个标准算子的详细定义可以参考『附录』中的『 NNAdapter 标准算子详细说明』章节,最新算子定义可以在 nnadapter.h 中查询。
NNAdapter Runtime¶
NNAdapter Runtime 的作用不仅是将 NNAdapter API 的调用翻译成模型、操作数、操作符的中间表达以及设备 HAL 层接口的调用,还包括设备 HAL 层库的注册、模型的多种设备间的异构和模型缓存的序列化和反序列化。
设备 HAL 层库的注册:用户进程的模型在某个设备上执行第一次推理时,会调用
NNAdapterDevice_acquire创建设备实例,此时, Runtime 的 DeviceManager 会发现该设备的 HAL 库没有被加载,就会通过设备名加载 HAL 库,然后根据 HAL 库规定的设备接口描述符号命名规则解析并获得该设备的设备接口描述实例的首地址,进而获得目标设备的基本信息和各功能函数地址,最后将它注册到DeviceManager由其统一管理。模型的多种设备间的异构:到目前为止,推理框架下发到 NNAdapter 的模型只能运行在某一种设备上,但为了进一步实现多种设备间的异构(即同一个硬件的不同运算单元,例如联发科芯片的 DSP 和 APU),我们预留了基于设备的操作符支持列表的模型子图分割处理过程。
模型缓存的序列化和反序列化:Runtime 通过设备 HAL 层库调用厂商 SDK 将模型编译、生成设备程序的过程的耗时通常比较长,它一般与模型规模成正比,与芯片 CPU 的处理能力成反比,例如
MobileNetV1模型在的 RK1808 芯片上的编译耗时大约在15秒左右,而ResNet50模型的耗时更是达到分钟级别。因此,模型的在线编译和生成将大大增加推理框架在用户进程启动后的第一次推理耗时,这在一些应用中是不可接受的,为了避免这个问题,NNAdapter Runtime 支持将已编译的设备代码缓存到设备的文件系统中,在下一次模型编译时将直接加载缓存文件进行恢复,其中就涉及缓存文件的序列化和反序列化过程。
NNAdapter HAL 标准接口定义¶
为了屏蔽硬件细节,向 NNAdapter Runtime 提供统一的设备访问接口,我们在 Runtime 和 厂商 SDK 之间建立了 NNAdapter HAL (即硬件抽象层),它是由 C 结构体实现的统一设备接口描述、模型、操作数和操作符的中间表达等数据结构组成,代码如下所示(访问 types.h 获得最新代码):
typedef struct Operand { NNAdapterOperandType type; void* buffer; uint32_t length; } Operand; typedef struct Argument { int index; void* memory; void* (*access)(void* memory, NNAdapterOperandType* type); } Argument; typedef struct Operation { NNAdapterOperationType type; std::vector<Operand*> input_operands; std::vector<Operand*> output_operands; } Operation; typedef struct Cache { const char* token; const char* dir; std::vector<NNAdapterOperandType> input_types; std::vector<NNAdapterOperandType> output_types; std::vector<uint8_t> buffer; } Cache; typedef struct Model { std::list<Operand> operands; std::list<Operation> operations; std::vector<Operand*> input_operands; std::vector<Operand*> output_operands; } Model; typedef struct Device { // Properties const char* name; const char* vendor; NNAdapterDeviceType type; int32_t version; // Interfaces int (*open_device)(void** device); void (*close_device)(void* device); int (*create_context)(void* device, const char* properties, void** context); void (*destroy_context)(void* context); int (*create_program)(void* context, Model* model, Cache* cache, void** program); void (*destroy_program)(void* program); int (*execute_program)(void* program, uint32_t input_count, Argument* input_arguments, uint32_t output_count, Argument* output_arguments); } Device;
模型、操作数和操作符的中间表达
为了实现 NNAdapter Runtime 和 NNAdapter HAL 对模型的统一表达,采用了较为简单的 C 结构体的表示方法定义了
Model(模型) 、Operand(操作数)和Operation(操作符):一个模型由若干个操作数和操作符组成,其中模型的输入、输出操作数被特殊标记,并按照顺序依次存储,但操作符不一定是按照拓扑顺序存储的。
可以借助 SortOperationsInTopologicalOrder 实现操作符的拓扑排序。例如在华为昇腾 HAL 层的 对多输出的算子插入 dummy 的 ADD 算子的优化器 ,需要首先调用 SortOperationsInTopologicalOrder 才能获得经过拓扑排序后的操作符列表。
为了方便调试,可以通过 Visualize 将模型数据结构输出为 DOT 格式字符串,将其复制到 webgraphviz 即可绘制模型拓扑结构。例如在华为昇腾 HAL 层的 打印优化前后的模型拓扑结构 代码。
一个操作符由操作符类型、输入、输出操作数列表组成,需要特别注意的是,操作数列表中的元素顺序需要严格按照操作符的定义的顺序依次存放。
设备接口描述
为 NNAdapter Runtune 在不同硬件提供统一的访问接口,需要对硬件的功能进行抽象和封装,涉及设备基本信息和标准功能接口,以下是昇腾 310 HAL 层设备接口描述结构体的实现(摘选自 driver.cc ):
... export "C" nnadapter::hal::Device huawei_ascend_npu = { .name = "huawei_ascend_npu", .vendor = "Huawei", .type = NNADAPTER_ACCELERATOR, .version = 1, .open_device = nnadapter::huawei_ascend_npu::OpenDevice, .close_device = nnadapter::huawei_ascend_npu::CloseDevice, .create_context = nnadapter::huawei_ascend_npu::CreateContext, .destroy_context = nnadapter::huawei_ascend_npu::DestroyContext, .create_program = nnadapter::huawei_ascend_npu::CreateProgram, .destroy_program = nnadapter::huawei_ascend_npu::DestroyProgram, .execute_program = nnadapter::huawei_ascend_npu::ExecuteProgram, };
在注册一个新的设备时,要求对
Device结构的所有成员进行赋值,特别是open_device、close_device到execute_program的函数指针的设置,这些函数被调用的时机如下图所示。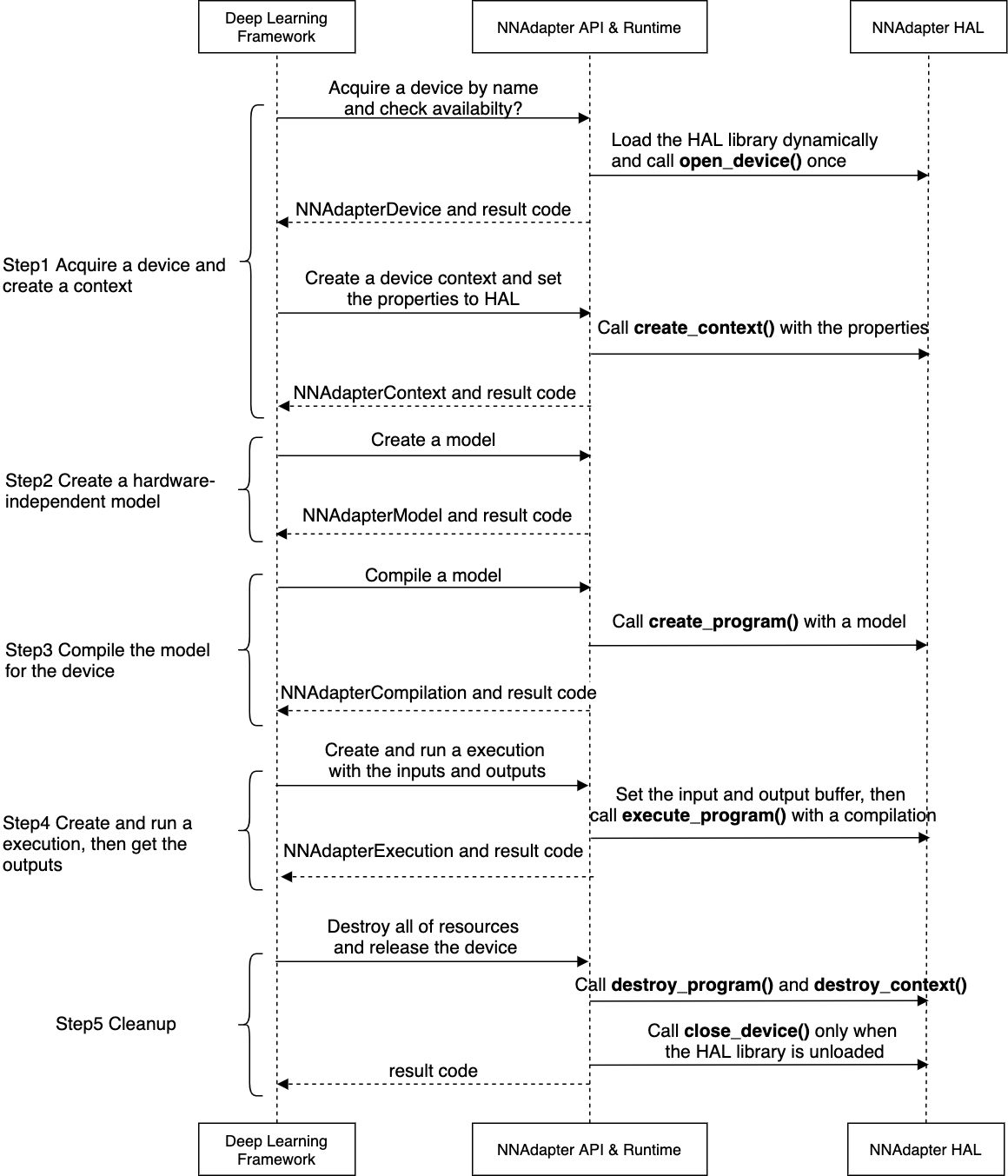
其详细过程可以参考下一章节的『应用程序、 Paddle Lite 、NNAdapter 和硬件 SDK 之间的详细调用过程』。
NNAdapter 在 Paddle Lite 的实现¶
Paddle Lite 、NNAdapter 各功能模块和已支持的硬件之间的关系¶
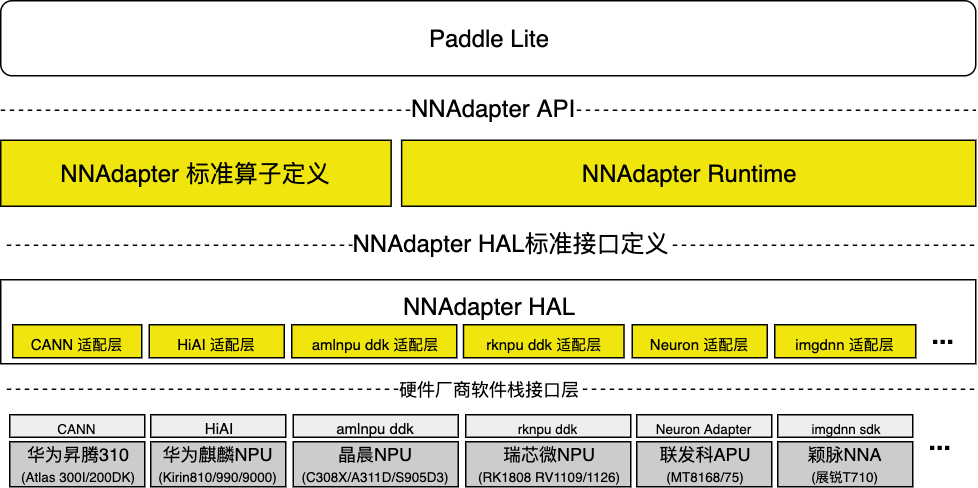
用户视角下各编译产物之间的调用关系¶
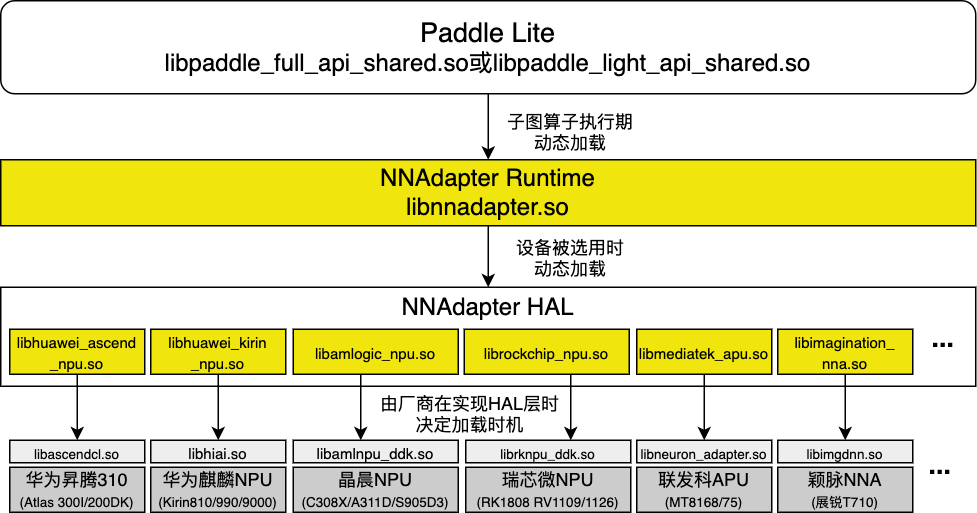
Paddle Lite 为 NNAdapter 新增的接口¶
设备查询和设置
check_nnadapter_device_name
bool check_nnadapter_device_name(const std::string& device_name)
通过设备名称查询设备是否可用,设备名称包括
huawei_ascend_npu,huawei_kirin_npu,amlogic_npu,rockchip_npu,mediatek_apu,imagination_nna等,已支持设备的最新列表可在 NNAdapter HAL 中查询。参数:
device_name:设备 HAL 层库的名称,例如: huawei_ascend_npu 。
返回值:设备可用则返回 TRUE 。
set_nnadapter_device_names
void set_nnadapter_device_names(const std::vector<std::string>& device_names)
设置模型在哪些设备中运行(当前版本只支持第一个设备)。
参数:
device_names:设备名称列表。
返回值:无。
设备上下文的参数设置
set_nnadapter_context_properties
void set_nnadapter_context_properties(const std::string& context_properties)
将设备参数传递给设备 HAL 层库。
参数:
context_properties:以 Key-value 字串的形式表示设备参数,例如:如果希望使用昇腾 310 卡的第 0 个核心,可以设置 “HUAWEI_ASCEND_NPU_SELECTED_DEVICE_IDS=0;” 。
返回值:无。
模型缓存
set_nnadapter_model_cache_dir
void set_nnadapter_model_cache_dir(const std::string& model_cache_dir)
启用模型编译缓存功能,设置编译后的设备程序的缓存文件(以 .nnc 为扩展名)的存储目录,它能够跳过每次进程启动且模型首次推理时的编译步骤,减少首次推理耗时。
参数:
model_cache_dir:模型缓存目录。
返回值:无。
set_nnadapter_model_cache_buffers
void set_nnadapter_model_cache_buffers(const std::string& model_cache_token, const std::vector<char>& model_cache_buffer)
设置模型缓存的标识和数据,子图在编译生成设备程序时,如果成功匹配到
model_cache_token,则跳过模型编译步骤,直接使用缓存数据恢复设备程序(需要设备 HAL 层库的支持),该接口通常用于从内存中设置解密后的模型缓存数据。参数:
model_cache_token:根据子图输入、输出、设备信息按照一定规则生成的唯一标识子图的 32 个字符,它实现方式可以参考相关代码。
model_cache_buffer:
model_cache_token对应子图和设备的模型缓存数据。
返回值:无。
自定义子图分割
set_nnadapter_subgraph_partition_config_path
void set_nnadapter_subgraph_partition_config_path(const std::string& subgraph_partition_config_path)
设置自定义子图分割配置文件路径,用于将某些算子强制异构到 CPU ,防止因切分成过多子图而导致的性能下降,内存增加。该配置文件的规则如下:
1)每行记录用于唯一标识某一个或某一类需要被强制异构到 CPU 的算子。
2)每行记录由『算子类型:输入张量名列表:输出张量名列表』组成,即以冒号分隔算子类型、输入和输出张量名列表,以逗号分隔输入、输出张量名列表中的每个张量名。
3)可省略输入、输出张量名列表中的部分张量名,如果不设置任何输入、输出张量列表,则代表计算图中该类型的所有算子节点均被强制异构到CPU。
用法举例:
op_type0:var_name0,var_name1:var_name2 表示将类型为 op_type0 、输入张量为 var_name0 和 var_name1 、输出张量为 var_name2 的算子强制异构到 CPU 上 op_type1::var_name3 表示将类型为 op_type1 、任意输入张量、输出张量为 var_name3 的算子强制异构到 CPU 上 op_type2:var_name4 表示将类型为 op_type2 、输入张量为 var_name4 、任意输出张量的算子强制异构到 CPU 上 op_type3 表示任意类型为 op_type3 的算子均被强制异构到CPU上
为了方便唯一标识模型中的某一个算子,可以在使用 cxxconfig 加载Paddle模型进行 nb 模型转换或直接推理时,设置 GLOG_v=5 打印完整调试信息,然后以
subgraph operators为关键字搜索,例如: ssd_mobilenet_v1_relu_voc_fp32_300 模型运行在华为麒麟 NPU 时,将得到如下调试信息:subgraph clusters: 1 digraph G { node_1150[label="batch_norm_0.tmp_3"] node_1154[label="batch_norm_1.tmp_3"] node_1190[label="batch_norm_10.tmp_3"] node_1194[label="batch_norm_11.tmp_3"] ... node_1426->node_1427 node_1427->node_1428 node_1428->node_1429 } // end G subgraph operators: feed:feed:image conv2d:image,conv1_weights,conv1_bn_offset:batch_norm_0.tmp_3 depthwise_conv2d:batch_norm_0.tmp_3,conv2_1_dw_weights,conv2_1_dw_bn_offset:batch_norm_1.tmp_3 conv2d:batch_norm_1.tmp_3,conv2_1_sep_weights,conv2_1_sep_bn_offset:batch_norm_2.tmp_3 ... box_coder:concat_0.tmp_0,concat_1.tmp_0,reshape2_0.tmp_0:box_coder_0.tmp_0 multiclass_nms:box_coder_0.tmp_0,transpose_12.tmp_0:save_infer_model/scale_0.tmp_0 fetch:save_infer_model/scale_0.tmp_0:fetch
其中:
1)
subgraph operators一行的后面是模型经过 Paddle Lite 各种优化 Pass 后的全部算子集合,可以非常方便的作为自定义子图分割配置文件的内容,这也将成为我们在硬件适配时快速调通目标模型的好帮手(即先将所有算子强制异构到 CPU 上,然后一行一行的删掉,让它们跑在目标设备上,这种方法可以快速定位问题算子,完成整个模型的调通)。2)
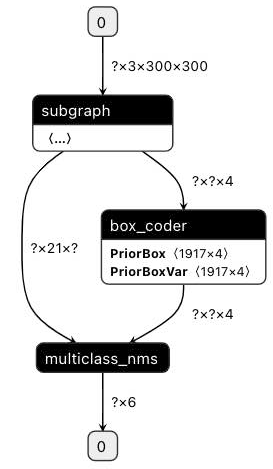
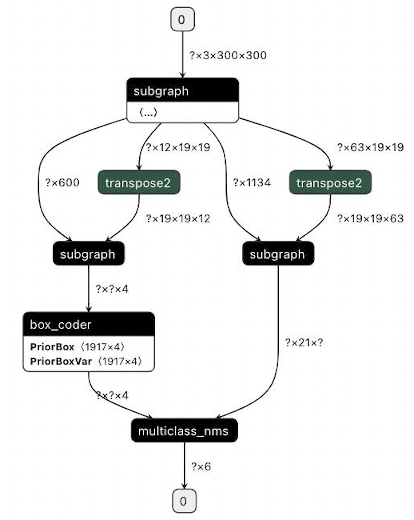
subgraph clusters一行的后面是经过子图检测后的子图个数,它下面从digraph G {开始到} // end G结束的部分则是用于可视化子图检测后的模型拓扑结构的 DOT 格式字符串,可将其复制到 webgraphviz 进行可视化,其中不同颜色的算子代表所属不同的子图。同样的,以 ssd_mobilenet_v1_relu_voc_fp32_300 为例,下面两张图展示了使用自定义子图分割配置前后的子图融合结果的对比:
1)未使用自定义子图分割配置:
2)使用如下自定义子图配置:
transpose2:conv2d_22.tmp_1:transpose_0.tmp_0,transpose_0.tmp_1 transpose2:conv2d_23.tmp_1:transpose_1.tmp_0,transpose_1.tmp_1
注意:该接口仅用于 cxxconfig 加载 Paddle 模型生成 nb 模型或直接推理时使用。
参数:
model_cache_token:根据子图输入、输出、设备信息按照一定规则生成的唯一标识子图的 32 个字符,它实现方式可以参考相关代码。
model_cache_buffer:
model_cache_token对应子图和设备的模型缓存数据。
返回值:无。
set_nnadapter_subgraph_partition_config_buffer
void set_nnadapter_subgraph_partition_config_buffer(const std::string& subgraph_partition_config_buffer)
设置自定义子图分割配置内容,该接口通常用于加、解密场景。
参数:
subgraph_partition_config_buffer:自定义子图分割配置的内容,与
set_nnadapter_subgraph_partition_config_path中阐述的一致。
返回值:无。
应用程序、 Paddle Lite 、NNAdapter 和硬件 SDK 之间的详细调用过程¶
提示:如果图片太小看不清,可以在图片上方点击右键并选择『在新标签页中打开该图片』。
查询设备是否可用,将设置的设备名称列表、设备上下文参数、模型缓存数据存储在 Paddle Lite 的 Scope 中( Scope 与 Predictor 绑定。通常存储模型的张量数据)。
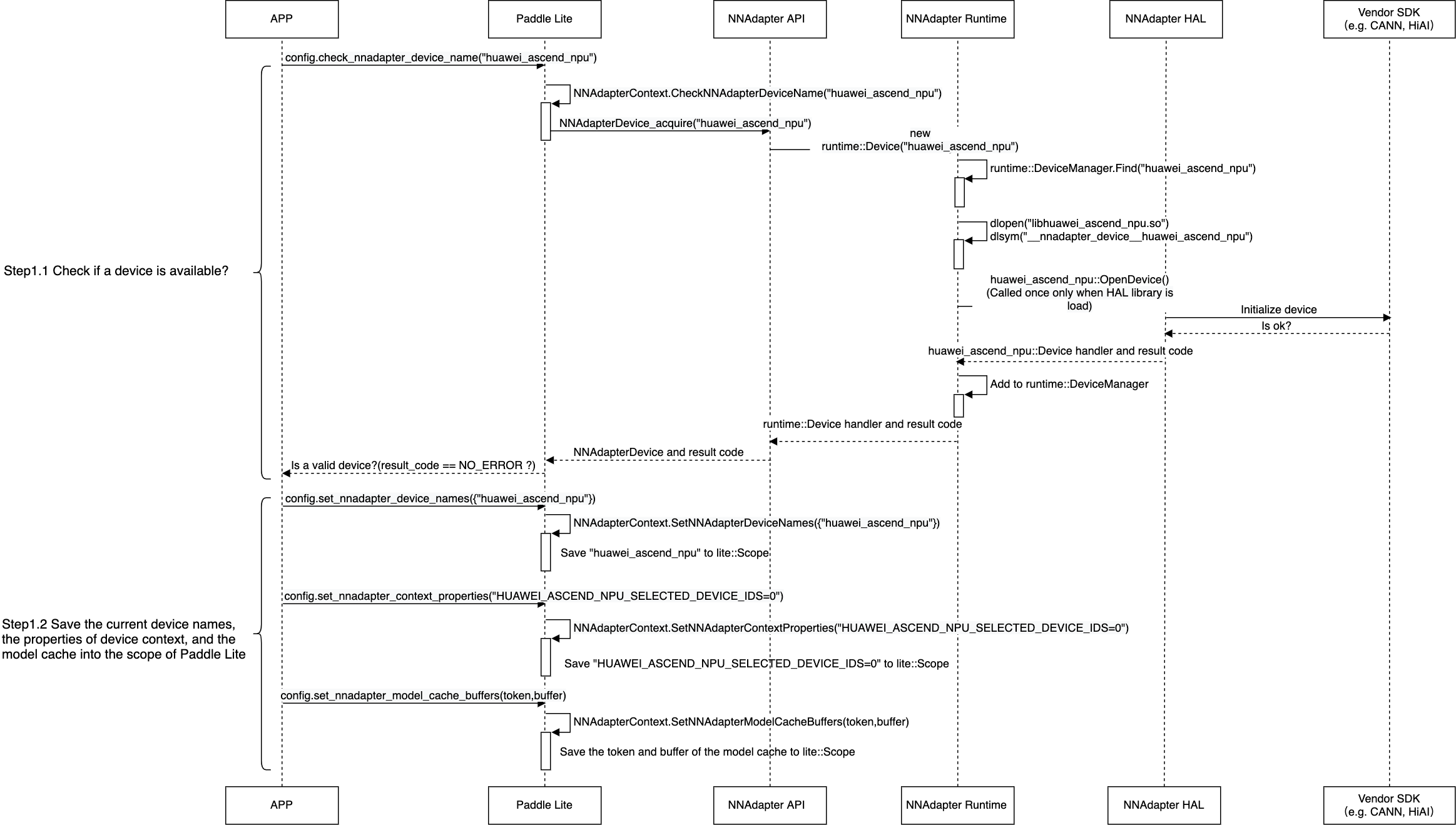
从 Scope 中获取设备名称列表、设备上下文参数,创建设备实例、设备统一上下文实例和与设备无关的模型实例。
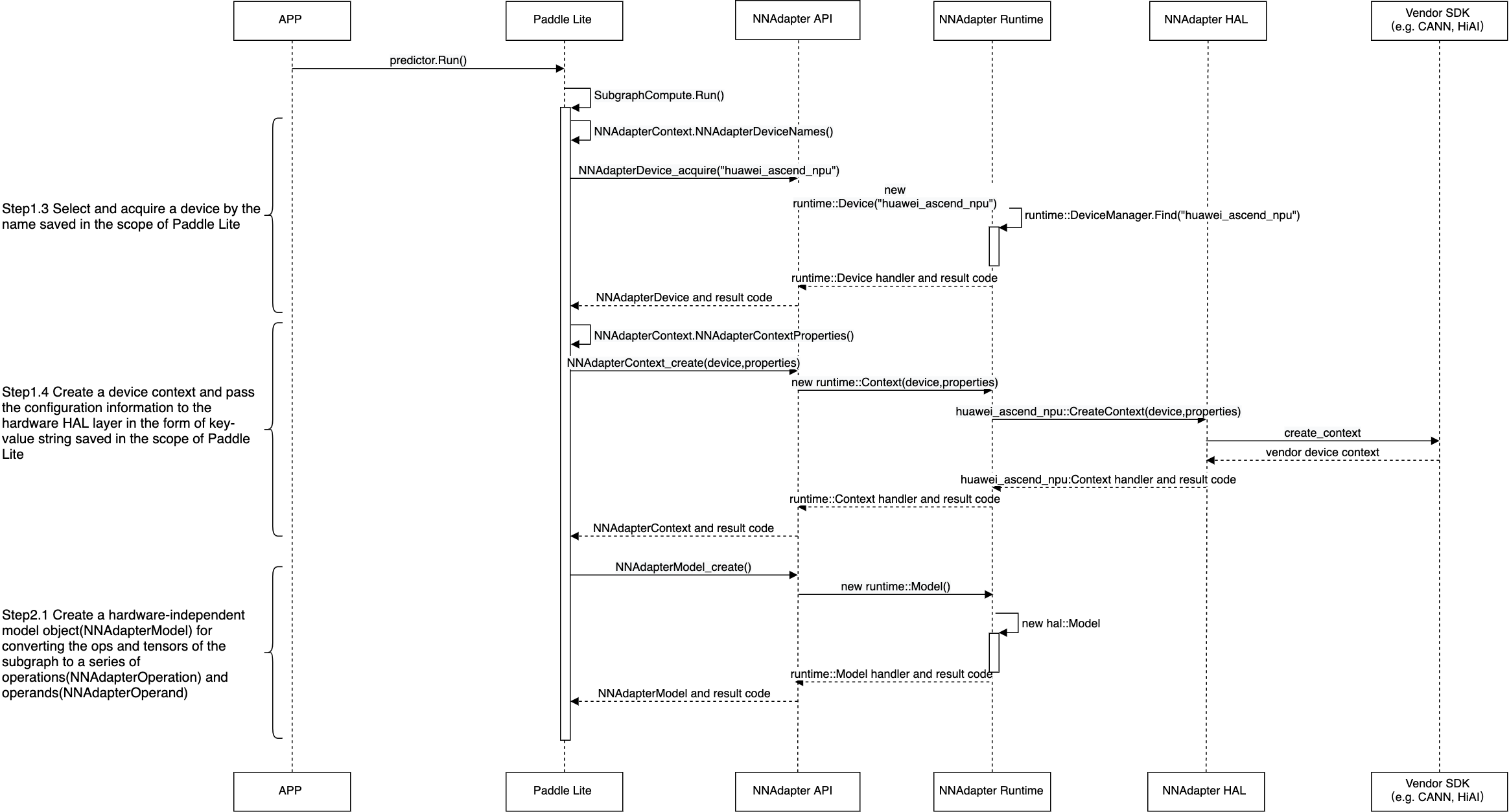
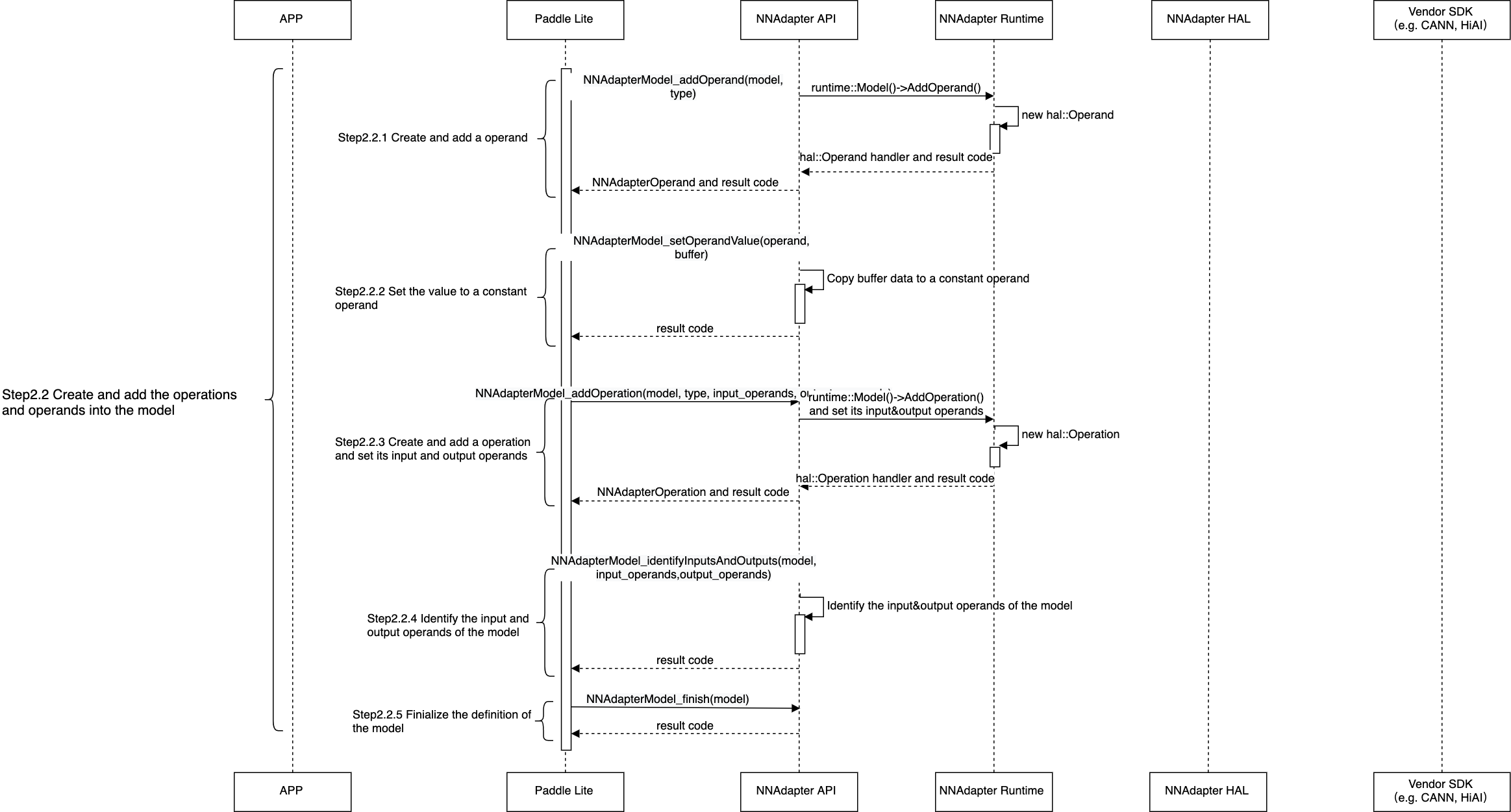
将 Paddle Lite 子图中的张量和算子全部转换为 NNAdapter 的操作数和操作符后加入到模型实例中。
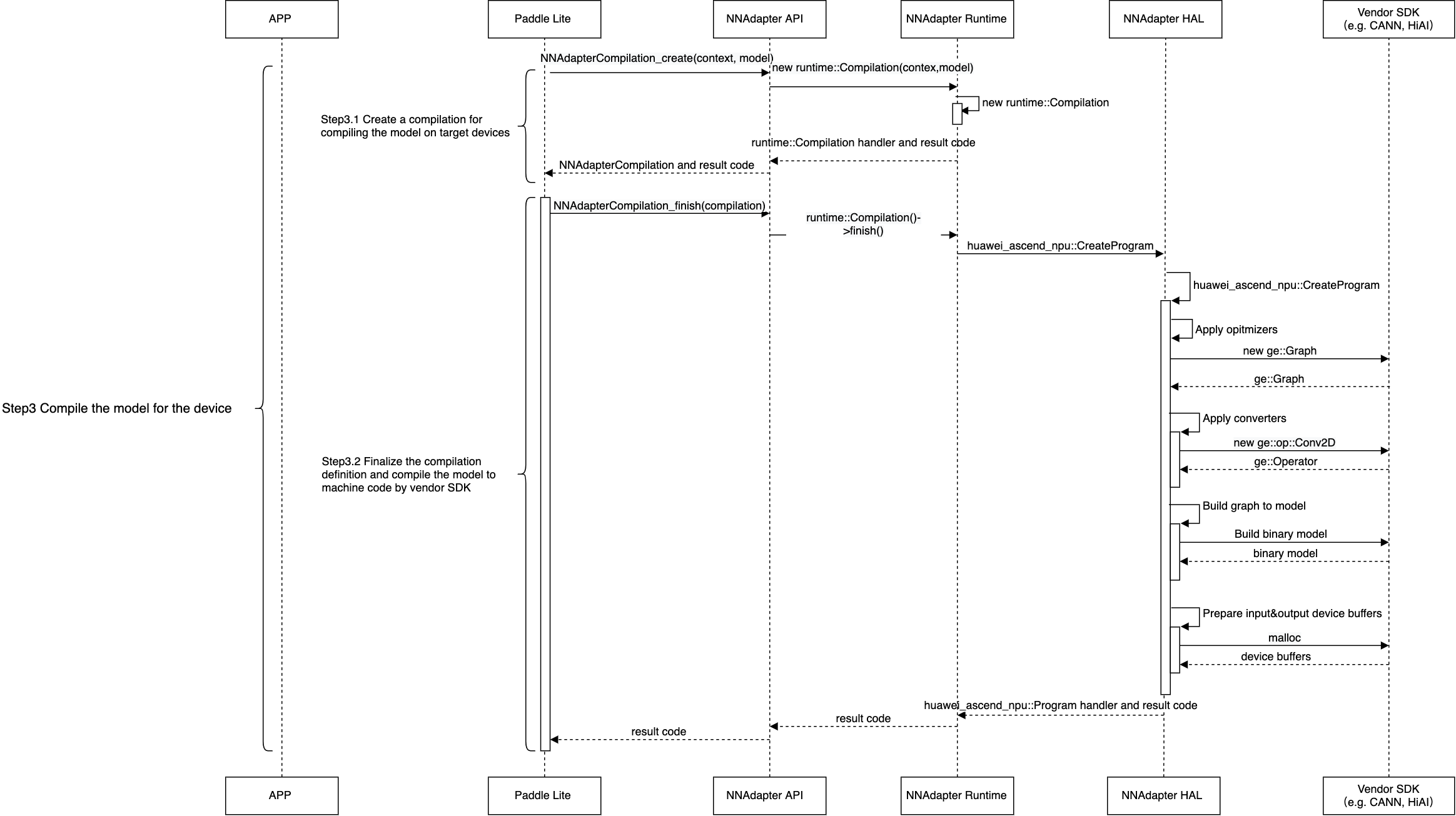
创建编译实例,从模型缓存中直接恢复设备程序,或通过目标设备的 HAL 层库调用硬件 SDK ,将模型实例编译生成设备程序。
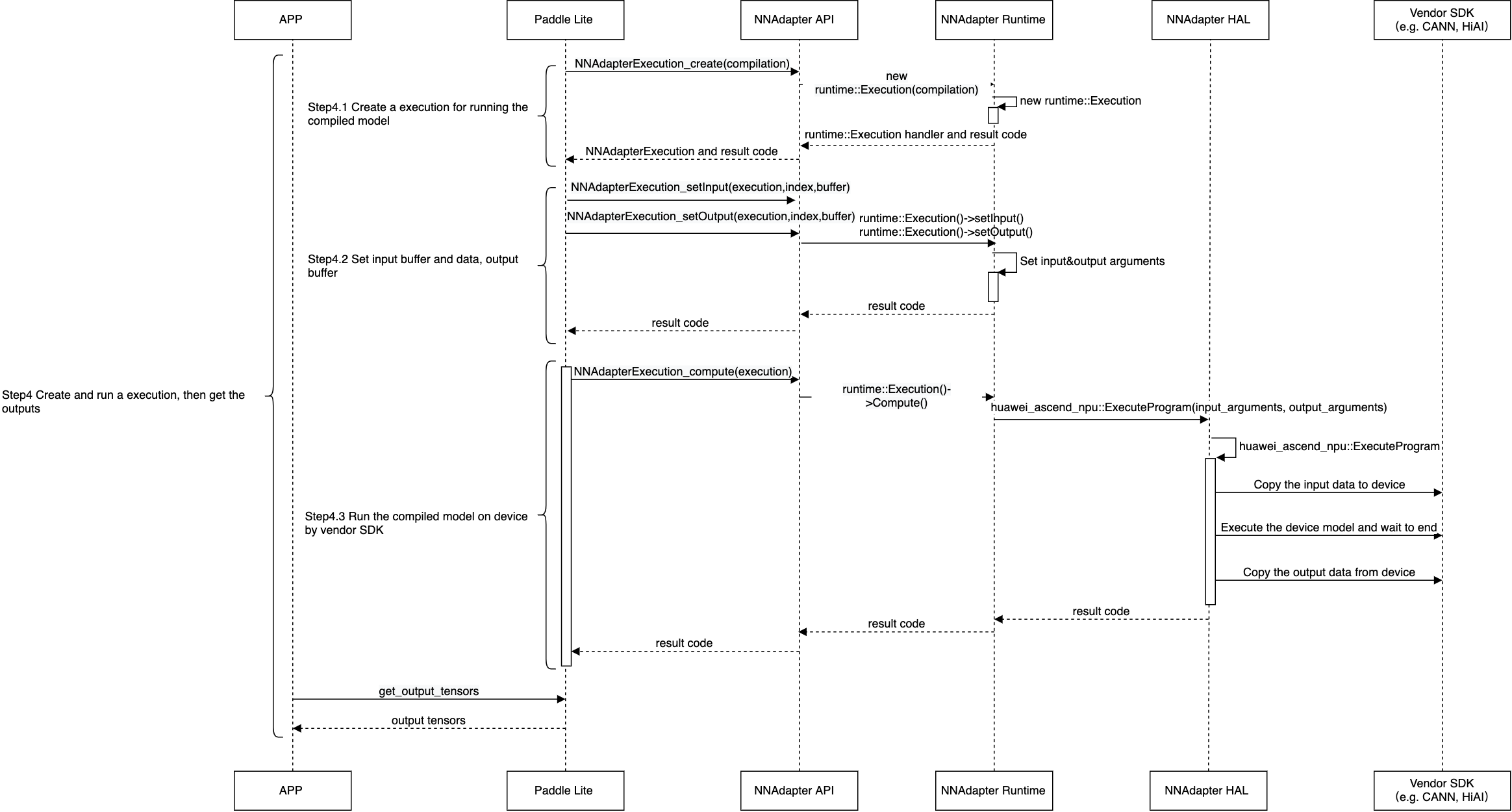
创建执行计划实例,设置输入、输出内存和访问函数,在设备程序执行完毕后,将结果返回给应用程序。
基于 NNAdapter 的硬件适配实践¶
一般流程¶
从 driver 目录中的复制一份 HAL 作为参考(服务端硬件可以参考华为昇腾 NPU
huawei_ascend_npu, SoC 类硬件可以参考晶晨 NPUamlogic_npu或 华为麒麟 NPUhuawei_kirin_npu)。基于参考硬件的 HAL 代码开发目标硬件的 HAL ,主要涉及 cmake 脚本的修改、 设备接口的实现(设备初始化、模型转换、编译和执行)。
模型转换:将 NNAdapter HAL 中的
Model转成厂商 SDK 中的模型的表示,其工作主要在于实现Operation到厂商 SDK 中的算子的表示的转换器,例如:华为昇腾 NPU HAL 中的NNADAPTER_ADD操作符到 CANN SDK 的ge::op::Add的转换,代码涉及以下三个部分:NNADAPTER_ADD 到 ge::op::Add 的转换器的实现 和 NNADAPTER_ADD 到 ge::op::Add 的转换器的注册 :在 HAL 层的
Model到厂商 SDK 模型转换步骤的Operation转换过程中,用于保证正确调用指定的转换器生成并添加厂商 SDK 的算子表示,进而基于厂商 SDK 完成模型转换。Paddle 算子 elementwise_add 到 NNADAPTER_ADD 转换器的注册 :具体是在转换器注册的设备名称字串中添加目标硬件的名称,其主要用于在 Paddle 模型的子图分割阶段中告诉子图分割算法哪些 Paddle 算子可以放在哪些硬件上执行,即哪些算子可以融合成一个 NNAdapter 子图,且在 NNAdapter 算子 Kernel 执行时,能够该子图转换为 NNAdapter 模型,进而传递到硬件的 HAL 层做进一步的转换。
基于 PaddleLite-generic-demo 跑通第一个分类模型:当目标硬件的 HAL 层代码开发完成后(前期仅需开发一个
NNADAPTER_SOFTMAX的转换器即可),需要验证 HAL 层到厂商 SDK 的链路是否打通,为方便厂商和用户测试,我们提供了包含图像分类和目标检测模型的 Demo 的压缩包,它支持 NNAdapter 目前已支持的所有硬件,覆盖 x86 Linux 、ARM Linux 和 Android 系统,可以本地执行或基于 ssh 或 adb 方式推送到远端设备上执行,各硬件的文档均涉及 Demo 的使用方法,具体可以访问:华为昇腾 NPU 、华为麒麟 NPU 、晶晨 NPU 、瑞芯微 NPU 、联发科 APU 和颖脉 NNA 等。模型、算子转换器调试方法:调试 Demo 中的模型有时候并不是一帆风顺,可能在模型转换过程中出现
core dump,也可能在模型跑通后发现结果无法与 CPU 结果对齐,这些问题尝尝源于部分 NNAdapter 操作符到厂商 SDK 算子的转换器的 BUG 导致的,有效的解决办法是:先将模型中所有 Paddle 算子强制跑在 CPU 上,然后根据模型拓扑顺序,逐步将 Paddle 算子放在目标硬件上执行,通过二分法、排除法最终定位到有问题的算子转换器上,具体可以参考上一章节中『自定义子图分割』。
添加算子、模型的单元测试
添加算子单元测试:为了持续验证每一个算子转化器能否正常工作,覆盖 Paddle 算子的所有功能,需要增加目标硬件的算子单元测试,具体步骤如下:
单元测试新增目标硬件的支持:增加目标硬件宏定义、单测设置目标硬件名称。
在目标算子单测增加宏定义和精度验证阈值,例如:在 softmax 单测增加华为昇腾 NPU 的支持,仅需添加 2 行代码。
添加模型单元测试:为了验证新合入的代码对已支持的模型是否有影响(正常跑通且精度对齐),需要在指定模型的单元测试中增加对目标硬件的支持,例如:在 MobileNetV1 模型增加华为昇腾 NPU 的支持,仅需添加 3~4 行代码(注意:全量化模型的单测为
test_mobilenet_v1_int8_per_channel_nnadapter和test_mobilenet_v1_int8_per_layer_nnadapter)。为了实现持续交付,需要向飞桨团队提供至少3套测试硬件,用于目标硬件的测试环境并加入到 Paddle Lite CI 系统。
增加硬件说明文档,例如:华为昇腾 NPU 的文档源码。
提交代码:具体是向 Paddle Lite 的 github 代码仓库发起 Pull request,具体可以参考新增硬件的『代码提交、Review 、合入机制、CI 机制』章节配置编译和代码提交环境,并按照规范提交代码,由飞桨团队同学 reivew 后方可合入主线代码。
附录¶
NNAdapter API 详细说明¶
NNAdapter_getVersion
int NNAdapter_getVersion(uint32_t* version)
获取 NNAdapter 版本值。
参数:
version:存储返回 NNAdapter 的版本值。
返回值:调用成功则返回 NNADAPTER_NO_ERROR 。
NNAdapterDevice_acquire
NNAdapterDevice_acquire(const char* name, NNAdapterDevice** device)
通过名称获取设备实例。
参数:
name:通过该名称加载并注册设备 HAL 库后(仅发生在进程首次调用时),创建一个设备实例。
device:存储创建后的设备实例。
返回值:调用成功则返回 NNADAPTER_NO_ERROR 。
NNAdapterDevice_release
NNAdapterDevice_release(NNAdapterDevice* device)
释放设备实例(注意:只有进程退出时,才会释放设备 HAL 层库)。
参数:
device:需要销毁的设备实例。
返回值:无。
NNAdapterDevice_getName
int NNAdapterDevice_getName(const NNAdapterDevice* device, const char** name)
获得设备名称。
参数:
device:设备实例。
name:存储返回的设备名称。
返回值:无。
NNAdapterDevice_getVendor
int NNAdapterDevice_getVendor(const NNAdapterDevice* device, const char** vendor)
获得设备厂商名称。
参数:
device:设备实例。
vendor:存储返回的设备厂商名称。
返回值:调用成功则返回 NNADAPTER_NO_ERROR 。
NNAdapterDevice_getType
int NNAdapterDevice_getType(const NNAdapterDevice* device, NNAdapterDeviceType* type)
获得设备类型。
参数:
device:设备实例。
type:存储返回的设备类型值,由
NNAdapterDeviceCode定义,NNADAPTER_CPU代表 CPU ,NNADAPTER_GPU代表 GPU ,NNADAPTER_ACCELERATOR代表神经网络加速器。
返回值:调用成功则返回 NNADAPTER_NO_ERROR 。
NNAdapterDevice_getVersion
int NNAdapterDevice_getVersion(const NNAdapterDevice* device, int32_t* version)
获取设备HAL动态链接库的版本值。
参数:
device:设备实例。
version:存储返回的设备 HAL 层库的版本值。
返回值:调用成功则返回 NNADAPTER_NO_ERROR 。
NNAdapterContext_create
int NNAdapterContext_create(NNAdapterDevice** devices, uint32_t num_devices, const char* properties, NNAdapterContext** context)
为多种设备创建一个统一设备上下文,并通过 Key-value 字符串的形式将设备的参数信息传递给每一个设备 HAL 层库。
参数:
devices:设备实例列表。
num_devices:
devices中设备实例的个数。properties:设备参数信息,按照 Key-value 字符串的形式表示设备参数信息,例如: “HUAWEI_ASCEND_NPU_SELECTED_DEVICE_IDS=0” 表示只使用昇腾 310 卡中第 0 个核心。
context:存储创建后的统一设备上下文实例。
返回值:调用成功则返回 NNADAPTER_NO_ERROR 。
NNAdapterContext_destroy
void NNAdapterContext_destroy(NNAdapterContext* context)
销毁统一设备上下文实例。
参数:
context:需要销毁的统一设备上下文实例。
返回值:无。
NNAdapterModel_create
int NNAdapterModel_create(NNAdapterModel** model)
创建一个空的、与设备无关的模型实例。
参数:
model:存储创建后的模型实例。
返回值:调用成功则返回 NNADAPTER_NO_ERROR 。
NNAdapterModel_destroy
void NNAdapterModel_destroy(NNAdapterModel* model)
销毁模型实例及相关资源。
参数:
model:需要销毁的模型实例。
返回值:无。
NNAdapterModel_finish
int NNAdapterModel_finish(NNAdapterModel* model)
结束模型组网。
参数:
model:模型实例。
返回值:调用成功则返回 NNADAPTER_NO_ERROR 。
NNAdapterModel_addOperand
int NNAdapterModel_addOperand(NNAdapterModel* model, const NNAdapterOperandType* type, NNAdapterOperand** operand)
向模型中增加一个操作数,即神经网络模型中的张量。
参数:
model:模型实例。
type:操作数的类型,由
NNAdapterOperandType定义,包含精度类型、数据布局、生命周期、维度信息和量化信息。operand:存储新增的操作数实例。
返回值:调用成功则返回 NNADAPTER_NO_ERROR 。
NNAdapterModel_setOperandValue
int NNAdapterModel_setOperandValue(NNAdapterOperand* operand, void* buffer, uint32_t length, bool copy)
设置常量操作数的值。
参数:
operand:操作数实例。
buffer:常量数据的内存地址。
lenght:常量数据的内存大小(字节)。
copy:是否创建常量数据的内存副本,否则将直接引用
buffer。后者要求在模型编译前都不允许修改buffer指向的内容。
返回值:调用成功则返回 NNADAPTER_NO_ERROR 。
NNAdapterModel_getOperandType
int NNAdapterModel_getOperandType(NNAdapterOperand* operand, NNAdapterOperandType** type)
查询操作数的类型。
参数:
operand:操作数实例。
type:存储返回的操作数类型。
返回值:调用成功则返回 NNADAPTER_NO_ERROR 。
NNAdapterModel_addOperation
int NNAdapterModel_addOperation(NNAdapterModel* model, NNAdapterOperationType type, uint32_t input_count, NNAdapterOperand** input_operands, uint32_t output_count, NNAdapterOperand** output_operands, NNAdapterOperation** operation)
向模型中增加一个操作符,并设置它的输入、输出操作数,即神经网络模型中的算子。
参数:
model:模型实例。
type:操作符类型,由
NNAdapterOperationCode定义,包含二维卷积NNADAPTER_CONV_2D,最大值池化NNADAPTER_AVERAGE_POOL_2D,均值池化NNADAPTER_MAX_POOL_2D等操作符。input_count:输入操作数的数量。
input_operands:输入操作数列表,需严格按照每一个操作符的定义依次将对应的输入操作数加入到列表中。
output_count:输出操作数的数量。
output_operands:输出操作数列表,需严格按照每一个操作符的定义依次将对应的输出操作数加入到列表中。
operation:存储新增的操作符实例。
返回值:调用成功则返回 NNADAPTER_NO_ERROR 。
NNAdapterModel_identifyInputsAndOutputs
int NNAdapterModel_identifyInputsAndOutputs(NNAdapterModel* model, uint32_t input_count, NNAdapterOperand** input_operands, uint32_t output_count, NNAdapterOperand** output_operands)
标识模型的输入、输出操作数,其生命周期将被标记为
NNADAPTER_MODEL_INPUT和NNADAPTER_MODEL_OUTPUT类型。参数:
model:模型实例。
input_count:输入操作数的数量。
input_operands:输入操作数列表,不约束每一个操作符顺序。
output_count:输出操作数的数量。
output_operands:输出操作数列表,不约束每一个操作符顺序。
返回值:调用成功则返回 NNADAPTER_NO_ERROR 。
NNAdapterCompilation_create
int NNAdapterCompilation_create(NNAdapterModel* model, const char* cache_token, void* cache_buffer, uint32_t cache_length, const char* cache_dir, NNAdapterContext* context, NNAdapterCompilation** compilation)
创建一个编译实例,基于指定的统一设备上下文,为多种设备(当前版本仅支持一种设备)编译模型实例或直接加载模型缓存。如果同时设置模型实例和模型缓存参数,则优先加载模型缓存,因此存在以下三种情况:
1)当设置
cache_token,cache_buffer和cache_length时,则直接从内存中加载模型缓存,此时将忽略model参数。2)当设置
cache_token和cache_dir时,将从 <cache_dir> 指定的目录中查找并尝试加载 <cache_token>.nnc 模型缓存文件,成功加载后将忽略model参数,否则在调用NNAdapterCompilation_finish完成模型实例model的在线编译后,在 <cache_dir> 目录中生成 <cache_token>.nnc 文件。3)当
cache_token,cache_buffer,cache_length和cache_dir均未被设置时,则在调用NNAdapterCompilation_finish后完成模型实例model的在线编译。需要注意的是,由于未设置cache_token和cache_dir,在编译完成后将不会生成模型缓存文件,将使得在模型首次推理时都会进行模型的在线编译,导致首次推理耗时过长。参数:
model:模型实例。
cache_token:模型缓存唯一标识。
cache_buffer:模型缓存的内存地址。
cache_length:模型缓存的内存大小(字节),必须与
cache_buffer成对使用。cache_dir:模型缓存的目录。
context:统一设备上下文实例。
compilation:存储创建的编译实例。
返回值:调用成功则返回 NNADAPTER_NO_ERROR 。
NNAdapterCompilation_destroy
void NNAdapterCompilation_destroy(NNAdapterCompilation* compilation)
销毁编译实例。
参数:
compilation:需要销毁的编译实例。
返回值:无。
NNAdapterCompilation_finish
int NNAdapterCompilation_finish(NNAdapterCompilation* compilation)
结束编译配置的设置,调用设备 HAL 层库对
NNAdapterCompilation_create中的模型实例model进行在线编译并生成设备程序。参数:
compilation:编译实例。
返回值:调用成功则返回 NNADAPTER_NO_ERROR 。
NNAdapterCompilation_queryInputsAndOutputs
int NNAdapterCompilation_queryInputsAndOutputs(NNAdapterCompilation* compilation, uint32_t* input_count, NNAdapterOperandType** input_types, uint32_t* output_count, NNAdapterOperandType** output_types)
查询编译后的模型的输入、输出操作数的数量和类型,必须在
NNAdapterCompilation_finish执行后才能调用,可以通过以下两次调用获得输入、输出操作数数量和类型信息。1)当
input_types和output_types为 NULL 时,则仅查询输入、输出操作数的数量并将值存储在input_count和output_count。2)当
input_types和output_types不为 NULL 时,则将输入、输出操作数的类型依次存储在input_types和output_types(要求调用方根据input_count和output_count分配它们的内存)。参数:
compilation:编译实例。
input_count:存储返回的输入操作数的数量,不允许为 NULL 。
input_types:存储返回的输入操作数列表。
output_count:存储返回的输出操作数的数量,不允许为 NULL 。
output_types:存储返回的输出操作数列表。
返回值:调用成功则返回NNADAPTER_NO_ERROR。
NNAdapterExecution_create
int NNAdapterExecution_create(NNAdapterCompilation* compilation, NNAdapterExecution** execution)
基于编译实例创建一个执行计划实例。
为了方便理解
NNAdapterCompilation和NNAdapterExecution的区别,可以将NNAdapterCompilation简单理解为已经编译好的设备代码,而NNAdapterExecution代表如何执行它,可以是顺序依次执行,也可以并行执行,可以是同步执行,也可以是异步执行,但目前 NNAdapter 仅支持同步顺序执行。参数:
compilation:编译实例。
execution:存储创建的执行计划实例。
返回值:调用成功则返回 NNADAPTER_NO_ERROR 。
NNAdapterExecution_destroy
void NNAdapterExecution_destroy(NNAdapterExecution* execution)
销毁执行计划实例。
参数:
execution:需要销毁的执行计划实例。
返回值:无。
NNAdapterExecution_setInput
int NNAdapterExecution_setInput(NNAdapterExecution* execution, int32_t index, void* memory, void* (*access)(void* memory, NNAdapterOperandType* type))
设置执行计划输入操作数的内存实例和访问函数。
为了能够让HAL层库更加灵活的访问推理框架的张量对象,在设置执行计划的输入时,要求设置内存实例
memory和内存实例访问函数access,例如:typedef struct { NNAdapterOperandPrecisionCode precision; uint32_t dimensions_count; int32_t dimensions_data[NNADAPTER_MAX_SIZE_OF_DIMENSIONS]; void* buffer; size_t length; } Memory; void* access_input_memory(void* memory, NNAdapterOperandType* type) { Memory* handle = reinterpret_cast<Memory*>(memory); // Return the dimensions and the host buffer to HAL memcpy(type->dimensions.data, handle->dimensions_data, handle->dimensions_count); return handle->buffer; } Memory input; NNAdapterExecution_setInput(execution, index, reinterpret_cast<void*>(&input), access_input_memory);
参数:
execution:执行计划实例。
index:模型输入操作数的索引。
memory:模型输入操作数的内存实例,不限定为具体的缓存首地址,用户可自行封装后通过 std::reinterpret_cast<void*>() 强制转为 void* 类型。
access:内存实例访问函数,HAL层库将通过
access函数访问memory获得 host 端缓存实际地址。
返回值:调用成功则返回 NNADAPTER_NO_ERROR 。
NNAdapterExecution_setOutput
int NNAdapterExecution_setOutput(NNAdapterExecution* execution, int32_t index, void* memory, void* (*access)(void* memory, NNAdapterOperandType* type))
设置执行计划输出操作数的内存实例和访问函数。
基于
NNAdapterExecution_setInput示例中的memory的定义实现输出内存实例的访问函数access:void* access_output_memory(void* memory, NNAdapterOperandType* type) { Memory* handle = reinterpret_cast<Memory*>(memory); // Get the buffer length according to the type->precision and type->dimensions size_t request_length = GetBufferLength(type); if (request_length > handle->length) { free(handle->buffer); handle->buffer = malloc(request_length); assert(handle->buffer); handle->length = request_length; } // Tell the inference framework the output dimensions and return the host buffer to HAL memcpy(handle->dimensions_data, type->dimensions.data, type->dimensions.count); handle->dimensions_count = type->dimensions.count; return handle->buffer; } Memory output; NNAdapterExecution_setOutput(execution, index, reinterpret_cast<void*>(&output), access_output_memory);
参数:
execution:执行计划实例。
index:模型输出操作数的索引。
memory:模型输出操作数的内存实例,不限定为具体的缓存首地址,用户可自行封装后通过 std::reinterpret_cast<void*>() 强制转为 void* 类型。
access:内存实例访问函数,HAL层库将通过
access函数访问memory获得 host 端缓存实际地址。
返回值:调用成功则返回 NNADAPTER_NO_ERROR 。
NNAdapterExecution_compute
int NNAdapterExecution_compute(NNAdapterExecution* execution)
同步调度执行计划实例。
参数:
execution:执行计划实例。
返回值:无。
NNAdapter 标准算子详细说明¶
NNADAPTER_ABS
Applies the abs activation to the input tensor element-wise. The output is calculated using this formula: output = abs(input)
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
Outputs:
0: output, the result with the same type as two inputs.
NNADAPTER_ADAPTIVE_AVERAGE_POOL_2D
Applies adaptive 2-D average pooling across the input according to input and output size.
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER 4-D tensor with shape [N, C_in, H_in, W_in].
1: output_shape, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64 tensor, with shape [2], with value [H_out, H_out].
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same shape and type as input.
NNADAPTER_ADAPTIVE_MAX_POOL_2D
Applies adaptive 2-D max pooling across the input according to input and output size.
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER 4-D tensor with shape [N, C_in, H_in, W_in].
1: output_shape, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64 tensor, with shape [2], with value [H_out, H_out].
2: return_indices, a NNADAPTER_BOOL8 scalar, whether to return index of output, default to false.
3: return_indices_dtype, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, must be one of NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64, specifies the dtype of the indices.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same shape and type as input.
1: indices, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64 tensor, with the same shape as output, indicates the indices of the current feature map.
NNADAPTER_ADD
Performs element-wise binary addition(with Numpy-style broadcasting https://numpy.org/doc/stable/user/basics.broadcasting.html).
Inputs:
0: input0, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: input1, a tensor with the same type as input0.
2: fuse_code, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, Specifies the activation to the result, must be one of NNAdapterFuseCode values.
Outputs:
0: output, the result with the same type as two inputs.
NNADAPTER_ARG_MAX
Computes the indices of the max elements of the input tensor’s element along the provided axis.
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: axis, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 scalar, the axis in which to compute the arg indices, it should be in range [-R, R), where R is the rank of input, negative value works the same way as axis+R.
2: keepdim, a NNADAPTER_BOOL8 scalar, keep the reduced dimension or not, If TRUE, keep the reduced dimension.
3: dtype, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, the value of NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64, specifies the dtype of the result,default to NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64.
Outputs:
0: output, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64 tensor.
NNADAPTER_ARG_MIN
Computes the indices of the min elements of the input tensor’s element along the provided axis.
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: axis, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 scalar. the axis in which to compute the arg indices, it should be in range [-R, R), where R is the rank of input, negative value works the same way as axis+R.
2: keepdim, a NNADAPTER_BOOL8 scalar, keep the reduced dimension or not, If TRUE, keep the reduced dimension.
3: dtype, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, the value of NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64, specifies the dtype of the result, default to NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64.
Outputs:
0: output, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64 tensor.
NNADAPTER_ASSIGN
Copy the input to the output.
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same shape and type as input.
NNADAPTER_EQUAL
Performs element-wise binary equal relational operation(with Numpy-style broadcasting https://numpy.org/doc/stable/user/basics.broadcasting.html). The output is calculated using this formula: output = input0 == input1
Inputs:
0: input0, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_BOOL8, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64,NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: input1, a tensor with the same type as input0.
Outputs:
0: output, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_BOOL8 tensor.
NNADAPTER_AVERAGE_POOL_2D
Applies a 2-D average pooling across the input according to kernel sizes, stride sizes, and pad lengths.
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER 4-D tensor with shape [N, C_in, H_in, W_in].
1: auto_pad, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar. 0 means “EXPLICIT” so that paddings is used. 1 means “SAME”. 2 means “VALID”. It must be one of NNAdapterAutoPadCode values.
2: pads, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 tensor, with shape [4] and data {height_top, height_bottom, width_left, width_right}, or with shape[0] and no data.
3: kernel_shape, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 tensor, with shape [2] and data {kernel_height, kernel_width}.
4: strides, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 tensor, with shape [2] and data {height_stride, width_stride}.
5: ceil_mode, a NNADAPTER_BOOL8 scalar, whether to use ceil or floor (default) to compute the output shape, default to false.
6: count_include_pad, a NNADAPTER_BOOL8 scalar, whether include pad pixels when calculating values for the edges, default to false.
7: fuse_code, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, must be one of NNAdapterFuseCode values.
Outputs:
0: output, the output 4-D tensor with shape [N, C_out, H_out, W_out], its type is the same as input.
When ceil_mode=false,
H_out = floor((H_in + padding_height_top + padding_height_bottom - filter_height) / stride_height + 1)
W_out = floor((W_in + padding_width_left + padding_width_right - filter_width) / stride_width + 1)
When ceil_mode=true,
H_out = ceil((H_in + padding_height_top + padding_height_bottom - filter_height) / stride_height + 1)
W_out = ceil((W_in + padding_width_left + padding_width_right - filter_width) / stride_width + 1)
NNADAPTER_BATCH_NORMALIZATION
Applies Batch Normalization over a 4D input (a mini-batch of 2D inputs with additional channel dimension) as described in the paper Batch Normalization: Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing Internal Covariate Shift.
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor with shape [N,C,…]
1: scale, a 1-D tensor with shape [C]. 1) If input’s type is NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, its type must be the same type.
2: bias, a 1-D tensor with shape [C]. 1) If input’s type is NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, its type must be the same type.
3: mean, a 1-D tensor with shape [C]. 1) If input’s type is NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, its type must be the same type.
4: variance, a 1-D tensor with shape [C]. 1) If input’s type is NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, its type must be the same type.
5: epsilon, a NNADAPTER_FLOAT32 scalar. Defaults to 1e-5. The small value added to the variance to prevent division by zero.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same shape and type as input.
NNADAPTER_CAST
The operator casts the elements of
inputto a data type specified by thedtypeargument.Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_BOOL8, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT8, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_UINT8, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT16, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT16, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT64 tensor.
1: dtype, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, the value of NNADAPTER_INT32, NNADAPTER_INT64, NNADAPTER_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_FLOAT64 etc. Specifies the dtype of the result.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same shape as input.
NNADAPTER_CLIP
Clip all elements in input into the range [min, max]. The output is calculated using this formula: output = MIN(MAX(input, min), max).
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: min, a 1-D tensor with the same type as input with shape[1].
2: max, a 1-D tensor with the same type as input with shape[1].
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same shape and type as input.
NNADAPTER_CONCAT
Concatenates a list of tensors into a single tensor along the given dimension. All input tensors must have the same shape, except for the dimension size of the axis to concatenate on.
Inputs:
0 ~ n-1: input0 ~ inputn-1, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: axis, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar. It represents the dimension along which axis to concat on. It should be in range [-R, R), where R is the rank of input, negative value works the same way as axis+R.
Outputs:
0: output, the result with the same type as the inputs.
NNADAPTER_CONV_2D
Performs a normal or depthwise 2-D convolution operation. The CONV_2D op computes a 2-D convolution based on the input, filter, strides, paddings, dilations, groups and etc.
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER 4-D tensor with shape [N, C_in, H_in, W_in].
1: filter, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_CHANNEL 4-D tensor.
For a normal convolution, the filter’s shape is [C_out, C_in, filter_height, filter_width], where C_out and C_in is the number of the channels of output and input, filter_height and filter_width is the filter’s kernel size in the ‘H’ and ‘W’ dimension.
For a depthwise convolution, the filter’s shape is [C_out, 1, filter_height, filter_width], where C_out is the number of the channels of output, filter_height and filter_width is the filter’s kernel size in the ‘H’ and ‘W’ dimension.
2: bias, a 1-D tensor with shape [C_out].
If input’s type is NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, its type must be the same type.
If filter’s type is NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER, its type should be NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT32_SYMM_PER_LAYER, and bias_scale == input_scale * filter_scale.
If filter’s type is NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_CHANNEL, its type should be NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT32_SYMM_PER_CHANNEL, and bias_scale[i] = input_scale * filter_scale[i] for each output channel.
3: auto_pad, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar. 0 means “EXPLICIT” so that paddings is used. 1 means “SAME”. 2 means “VALID”. It must be one of NNAdapterAutoPadCode.
4: pads, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 tensor, with shape [4] and data {height_top, height_bottom, width_left, width_right}, or with shape[0] and no data.
5: strides, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 tensor, with shape [2] and data {height_stride, width_stride}.
6: group, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar.
For a normal convolution, group must be 1.
For a depthwise convolution, the formula should be satisfied: group=C_out=C_in.
7: dilations, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 tensor, with shape [2] and data {dilations_height, dilations_width}.
8: fuse_code, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, must be one of NNAdapterFuseCode values.
Outputs:
0: output, the output 4-D tensor with shape [N, C_out, H_out, W_out], its type is the same as input.
H_out = (H_in + padding_height_top + padding_height_bottom - (dilation_height * (filter_height - 1) + 1)) / stride_height + 1
W_out = (W_in + padding_width_left + padding_width_right - (dilation_width * (filter_width - 1) + 1)) / stride_width + 1
NNADAPTER_CONV_2D_TRANSPOSE
Performs the transpose of 2-D convolution operation(also called deconvolution) based on the input, filter, strides, paddings, dilations, groups and etc.
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER 4-D tensor with shape [N, C_in, H_in, W_in].
1: filter, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_CHANNEL 4-D tensor. The filter’s shape is [C_out, C_in, filter_height, filter_width], where C_out and C_in is the number of the channels of output and input, filter_height and filter_width is the filter’s kernel size in the ‘H’ and ‘W’ dimension.
2: bias, a 1-D tensor with shape [C_out].
If input’s type is NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, its type must be the same type.
If filter’s type is NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER, its type should be NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT32_SYMM_PER_LAYER, and bias_scale == input_scale * filter_scale.
If filter’s type is NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_CHANNEL, its type should be NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT32_SYMM_PER_CHANNEL, and bias_scale[i] = input_scale * filter_scale[i] for each output channel.
3: auto_pad, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar. 0 means “EXPLICIT” so that paddings is used. 1 means “SAME”. 2 means “VALID”. It must be one of NNAdapterAutoPadCode.
4: pads, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 tensor, with shape [4] and data {height_top, height_bottom, width_left, width_right}, or shape[0] and no data.
5: strides, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 tensor, with shape [2] and data {height_stride, width_stride}.
6: group, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar.
For a normal convolution, group must be 1.
For a depthwise convolution, the formula should be satisfied: group=C_out=C_in.
7: dilations, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 tensor, with shape [2] and data {dilations_height, dilations_width}.
8: output_padding, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 tensor, with shape [2] and data {output_pad_height, output_pad_width}, or shape[0] and no data.
9: output_shape, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64 tensor, with shape [2] and data {output_height, output_width}, or shape[0] and no data.
10: fuse_code, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, must be one of NNAdapterFuseCode values.
Outputs:
0: output, the output 4-D tensor with shape [N, C_out, H_out, W_out], its type is the same as input.
H_out = (H_in - 1) * stride_height - padding_height_top - padding_height_bottom + (dilation_height * (filter_height - 1)) + 1 + output_padding_height
W_out = (W_in - 1) * stride_width - padding_width_left - padding_width_right + (dilation_width * (filter_width - 1) + 1)) + 1 + output_padding_width
NNADAPTER_CUM_SUM
Performs cumulative sum of the input elements along the given axis.
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: axis, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, default to -1. It represents the dimension along which softmax will be performed. It should be in range [-R, R), where R is the rank of input, negative value works the same way as axis+R.
2: exclusive, a NNADAPTER_NOOL8 scalar. If set to true, the top element will not be include, default to false.
3: reverse, a NNADAPTER_NOOL8 scalar, whether to perform the cumsum in the reversed direction, default to false.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same type as input.
NNADAPTER_DEFORMABLE_CONV_2D
Compute 2-D deformable convolution on 4-D input.
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER 4-D tensor with shape [N, C_in, H_in, W_in].
1: offset, a tensor with the same type as input. It’s shape is [N, 2 * deformable_groups * H_f * W_f, H_in, W_in].
2: mask, a tensor with the same type as input. It’s shape is [N, deformable_groups * H_f * W_f, H_in, W_in].
3: filter, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_CHANNEL 4-D tensor.
For a normal convolution, the filter’s shape is [C_out, C_in, filter_height, filter_width], where C_out and C_in is the number of the channels of output and input, filter_height and filter_width is the filter’s kernel size in the ‘H’ and ‘W’ dimension.
For a depthwise convolution, the filter’s shape is [C_out, 1, filter_height, filter_width], where C_out is the number of the channels of output, filter_height and filter_width is the filter’s kernel size in the ‘H’ and ‘W’ dimension.
4: bias, a 1-D tensor with shape [C_out].
If input’s type is NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, its type must be the same type.
If filter’s type is NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER, its type should be NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT32_SYMM_PER_LAYER, and bias_scale == input_scale * filter_scale.
If filter’s type is NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_CHANNEL, its type should be NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT32_SYMM_PER_CHANNEL, and bias_scale[i] = input_scale * filter_scale[i] for each output channel.
5: pads, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 tensor, with shape [4] and data {height_top, height_bottom, width_left, width_right}, or with shape[0] and no data.
6: strides, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 tensor, with shape [2] and data {height_stride, width_stride}.
7: group, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar.
For a normal convolution, group must be 1.
For a depthwise convolution, the formula should be satisfied: group=C_out=C_in.
8: deformable_group, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar. Specify the c-axis grouping number of input.
9: dilations, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 tensor, with shape [2] and data {dilations_height, dilations_width}.
10: fuse_code, A NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, must be one of NNAdapterFuseCode values.
Outputs:
0: output, the output 4-D tensor with shape [N, C_out, H_out, W_out], its type is the same as input.
H_out = (H_in + padding_height_top + padding_height_bottom - (dilation_height * (filter_height - 1) + 1)) / stride_height + 1
W_out = (W_in + padding_width_left + padding_width_right - (dilation_width * (filter_width - 1) + 1)) / stride_width + 1
NNADAPTER_DIV
Performs element-wise binary division(with Numpy-style broadcasting https://numpy.org/doc/stable/user/basics.broadcasting.html).
Inputs:
0: input0, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: input1, a tensor with the same type as input0.
2: fuse_code, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, Specifies the activation to the result, must be one of NNAdapterFuseCode values.
Outputs:
0: output, the result with the same type as two inputs.
NNADAPTER_EXP
Applies the exp activation to the input tensor element-wise. The output is calculated using this formula: output = e^input
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
Outputs:
0: output, the result with the same type as two inputs.
NNADAPTER_EXPAND
Broadcast the input tensor following the given shape(by Numpy-style broadcasting https://numpy.org/doc/stable/user/basics.broadcasting.html).
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: shape, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64 tensor. It indicates the shape you want to expand to, following the broadcast rule.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same type as input.
NNADAPTER_FILL
Produces a tensor with the
shapeandvalue.Inputs:
0: shape, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64 tensor.
1: value, a NNADAPTER_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_INT32, NNADAPTER_INT64 or NNADAPTER_BOOL scalar.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the
shapeandvalue.
NNADAPTER_FLATTEN
Flattens the input tensor according to a contiguous range of axes from
start_axistostop_axis.Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: start_axis, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, the start axis to flatten.
2: end_axis, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, the end axis to flatten.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same type as input.
NNADAPTER_FULLY_CONNECTED
Add a fully connected layer. The output is calculated using this formula: output = activation(input * weight’ + bias).
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor of at least rank 2, If its rank is greater than 2, it will be flattened to a 2-D Tensor with the shape [batch_size, input_size], where input_size represents the number of inputs, matching the second dimension of weight, and batch_size is calculated by dividing the number of elements by input_size.
1: weight, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_CHANNEL 2-D tensor with shape [num_units, input_size], where the num_units represents the number of output units, which also means the feature size of output.
2: bias, a 1-D tensor with shape [num_units].
If input’s type is NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, its type must be the same type.
If weight’s type is NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER, its type should be NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT32_SYMM_PER_LAYER, and bias_scale == input_scale * weight_scale.
If weight’s type is NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_CHANNEL, its type should be NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT32_SYMM_PER_CHANNEL, and bias_scale[i] = input_scale * weight_scale[i] for each output channel.
3: fuse_code, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, must be one of NNAdapterFuseCode values.
Outputs:
0: output, a 2-D tensor with shape [batch_size, num_units], and its type is the same as input.
NNADAPTER_GATHER
Gathers entries of axis dimension of
inputindexed byindices, and concatenates them together.Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor, of any rank R.
1: indices, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64 tensor, of any rank Q. All index values are expected to be within bounds [-S, S-1] along axis of size S.
2: axis, A NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar. It represents the dimension along which gather will be performed. It should be in range [-R, R), where R is the rank of input, negative value works the same way as axis+R.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same type as input, of rank with rank Q + (R - 1).
NNADAPTER_GELU
Applies the Gaussian Error Linear Units activation to the input tensor element-wise. Refer to https://arxiv.org/abs/1606.08415 for more details.
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: approximate, a NNADAPTER_BOOL8 scalar, whether to enable approximation.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same shape and type as input.
NNADAPTER_GREATER
Performs element-wise binary greater relational operation(with Numpy-style broadcasting https://numpy.org/doc/stable/user/basics.broadcasting.html): output = input0 > input1.
Inputs:
0: input0, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_BOOL8, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64,NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: input1, a tensor with the same type as input0.
Outputs:
0: output, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_BOOL8 tensor.
NNADAPTER_GREATER_EQUAL
Performs element-wise binary greater_equal relational operation(with Numpy-style broadcasting https://numpy.org/doc/stable/user/basics.broadcasting.html): output = input0 >= input1.
Inputs:
0: input0, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_BOOL8, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: input1, a tensor with the same type as input0.
Outputs:
0: output, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_BOOL8 tensor.
NNADAPTER_HARD_SIGMOID
Applies the hard-sigmoid activation to the input tensor element-wise. The output is calculated using this formula: output = max(0, min(1, alpha * input + beta)).
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: alpha, a NNADAPTER_FLOAT32 scalar.
2: beta, a NNADAPTER_FLOAT32 scalar.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same shape and type as input.
NNADAPTER_HARD_SWISH
Applies the hard-swish activation to the input tensor element-wise. The output is calculated using this formula: output = input * max(0, min(1, alpha * input + beta)).
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: alpha, a NNADAPTER_FLOAT32 scalar.
2: beta, a NNADAPTER_FLOAT32 scalar.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same shape and type as input.
NNADAPTER_INSTANCE_NORMALIZATION
Applies Instance Normalization over a N-D input (N>2) as described in the paper https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.08022. output = scale * (input - mean) / sqrt(variance + epsilon) + bias, where mean and variance are computed per instance per channel.
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor with shape [N,C,…].
1: scale, a tensor, with shape [C].
If input’s type is NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, its type must be the same type.
2: bias, a tensor with the same shape as scale.
If input’s type is NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, its type must be the same type.
3: epsilon, a NNADAPTER_FLOAT32 scalar, the small value added to the variance to prevent division by zero, default to 1e-5.
4: fuse_code, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, must be one of NNAdapterFuseCode values.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same shape and type as input.
NNADAPTER_LAYER_NORMALIZATION
Applies Layer Normalization over a N-D input described in the paper Layer Normalization: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1607.06450v1.pdf.
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor with shape [N,C,…].
1: scale, a tensor, shape is performed along the input dimension from begin_norm_axis to the rank of input.
If input’s type is NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, its type must be the same type.
2: bias, a tensor with the same shape as scale.
If input’s type is NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, its type must be the same type.
3: begin_norm_axis, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, indicates that the normalization will be performed along the dimension from begin_norm_axis to the rank of input, default to 1.
4: epsilon, a NNADAPTER_FLOAT32 scalar, default to 1e-5.
5: fuse_code, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, must be one of NNAdapterFuseCode values.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same shape and type as input.
NNADAPTER_LEAKY_RELU
Applies the Leaky ReLU activation to the input tensor element-wise. The output is calculated using this formula: output = input, if input >=0; output = alpha * input, if input < 0.
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: alpha, a NNADAPTER_FLOAT32 scalar.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same shape and type as input.
NNADAPTER_LESS
Performs element-wise binary less relational operation(with Numpy-style broadcasting https://numpy.org/doc/stable/user/basics.broadcasting.html): output = input0 < input1.
Inputs:
0: input0, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_BOOL8, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: input1, a tensor with the same type as input0.
Outputs:
0: output, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_BOOL8 tensor.
NNADAPTER_LESS_EQUAL
Performs element-wise binary less_equal relational operation(with Numpy-style broadcasting https://numpy.org/doc/stable/user/basics.broadcasting.html): output = input0 <= input1.
Inputs:
0: input0, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_BOOL8, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64,NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: input1, a tensor with the same type as input0.
Outputs:
0: output, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_BOOL8 tensor.
NNADAPTER_LOG
Applies the log activation to the input tensor element-wise. The output is calculated using this formula: output = log(input).
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same shape and type as input.
NNADAPTER_LP_NORMALIZATION
Applies the Lp Normalization to the input tensor element-wise. The output is calculated using this formula: output = input / (sum(abs(input)) + epsilon), if p = 1; output = input / (sqrt(sum(input^2)) + epsilon), if p = 2.
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: axis, an 1-D NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32, default to [1]. It represents the dimension along which norm will be performed. It should be in range [-R, R), where R is the rank of input, negative value works the same way as axis + R.
2: p, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar. The exponent value in the norm formulation, only 1 or 2 are supported, default to 2.
3: epsilon, a NNADAPTER_FLOAT32 scalar, specifying the lower limit of normalization.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same shape and type as input.
NNADAPTER_MAT_MUL
Matrix product that behaves like numpy.matmul.
Inputs:
0: input0, A NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: input1, a tensor with the same type as input0.
2: transpose_input0, a NNADAPTER_BOOL8 scalar, whether to transpose the last two dimensions of input0 before multiplication.
3: transpose_input1, a NNADAPTER_BOOL8 scalar, whether to transpose the last two dimensions of input1 before multiplication.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same type as two inputs.
NNADAPTER_MAX
Performs element-wise binary maximum(with Numpy-style broadcasting https://numpy.org/doc/stable/user/basics.broadcasting.html).
Inputs:
0: input0, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: input1, a tensor with the same type as input0.
2: fuse_code, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, specifies the activation to the result, must be one of NNAdapterFuseCode values.
Outputs:
0: output, the result with the same type as two inputs.
NNADAPTER_MAX_POOL_2D
Applies a 2-D max pooling across the input according to kernel sizes, stride sizes, and pad lengths.
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER 4-D tensor with shape [N, C_in, H_in, W_in].
1: auto_pad, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar. 0 means ‘EXPLICIT’ so that paddings is used. 1 means ‘SAME’. 2 means ‘VALID’. It must be one of NNAdapterAutoPadCode values.
2: pads, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 tensor, with shape [4] and data {height_top, height_bottom, width_left, width_right}, or with shape[0] and no data.
3: kernel_shape, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 tensor, with shape [2] and data {kernel_height, kernel_width}.
4: strides, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 tensor, with shape [2] and data {height_stride, width_stride}.
5: ceil_mode, a NNADAPTER_BOOL8 scalar, whether to use ceil(true) or floor(false) to compute the output shape, default to false.
6: return_indices, A NNADAPTER_BOOL8 scalar, whether to return index of output, default to false.
7: return_indices_dtype, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, must be one of NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64, specifies the dtype of the indices.
8: fuse_code, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, must be one of NNAdapterFuseCode values.
Outputs:
0: output, the output 4-D tensor with shape [N, C_out, H_out, W_out], its type is the same as input.
When ceil_mode=false,
H_out = floor((H_in + padding_height_top + padding_height_bottom - filter_height) / stride_height + 1)
W_out = floor((W_in + padding_width_left + padding_width_right - filter_width) / stride_width + 1)
When ceil_mode=true,
H_out = ceil((H_in + padding_height_top + padding_height_bottom - filter_height) / stride_height + 1)
W_out = ceil((W_in + padding_width_left + padding_width_right - filter_width) / stride_width + 1)
1: indices, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64 tensor, with the same shape as output, indicates the indices of the current feature map.
NNADAPTER_MIN
Performs element-wise binary minimum(with Numpy-style broadcasting https://numpy.org/doc/stable/user/basics.broadcasting.html).
Inputs:
0: input0, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: input1, a tensor with the same type as input0.
2: fuse_code, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, specifies the activation to the result, must be one of NNAdapterFuseCode values.
Outputs:
0: output, the result with the same type as two inputs.
NNADAPTER_MUL
Performs element-wise binary multiplication(with Numpy-style broadcasting https://numpy.org/doc/stable/user/basics.broadcasting.html).
Inputs:
0: input0, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: input1, a tensor with the same type as input0.
2: fuse_code, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, specifies the activation to the result, must be one of NNAdapterFuseCode values.
Outputs:
0: output, the result with the same type as two inputs.
NNADAPTER_NOT_EQUAL
Performs element-wise binary not_equal relational operation(with Numpy-style broadcasting https://numpy.org/doc/stable/user/basics.broadcasting.html). The output is calculated using this formula: output = input0 != input1.
Inputs:
0: input0, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_BOOL8, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: input1, a tensor with the same type as input0.
Outputs:
0: output, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_BOOL8 tensor.
NNADAPTER_PAD
Pads input according to the specified
pads,modeandvalue.Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: pads, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 1-D tensor, with shape [2 * input_rank], with value [x0_begin, x0_end, x1_begin, x1_end,…].
2: mode, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, supported pad modes:
constant(default),reflect,edge, should be a value of NNAdapterPadModeCode.3: value, a scalar with the same type as input, only be used if the mode is
constant.
Outputs:
0: output, the result with the same type as input.
NNADAPTER_POW
Performs element-wise binary pow(with Numpy-style broadcasting https://numpy.org/doc/stable/user/basics.broadcasting.html). The output is calculated using this formula: output = input0^input1.
Inputs:
0: input0, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: input1, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
2: fuse_code, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, specifies the activation to the result, must be one of NNAdapterFuseCode values.
Outputs:
0: output, the result with the same type as input.
NNADAPTER_PRELU
Applies the prelu activation to the input tensor. The output is calculated using this formula: output = input, if input >= 0; output = slope * input, if input < 0.
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32 or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor with shape [N, C, …].
1: slope, a tensor, with shape [1] or [C].
If input’s type is NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, its type must be the same type.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same shape and type as input.
NNADAPTER_RANGE
Produces a 1-D tensor with values from
starttoendwith stepstep.Inputs:
0: start, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor with shape[1].
1: end, a tensor with the same shape and type as
start.2: step, a tensor with the same shape and type as
start.
Outputs:
0: output, a 1-D tensor with the same type as
start.
NNADAPTER_REDUCE_MEAN
Computes the mean of the input’s elements along the specified axis. If axis has no data, mean is calculated over all elements of input. If keepdims equal 0, the resulted tensor have the reduced dimension pruned.
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: axes, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 tensor, indicates the dimensions to perform mean calculations. It should be in range [-R, R), where R is the rank of input, negative value works the same way as axis+R. If axis has no data, mean is calculated over all elements of input.
2: keepdim, a NNADAPTER_BOOL8 scalar, keeps the reduced dimension or not, default to true.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same type as input.
NNADAPTER_RELU
Applies rectified linear activation to the input tensor element-wise. The output is calculated using this formula: output = max(0, input).
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same shape and type as input.
NNADAPTER_RELU6
Applies rectified linear 6 activation to the input tensor element-wise. The output is calculated using this formula: output = min(6, max(0, input)).
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same shape and type as input.
NNADAPTER_RESHAPE
Reshapes a tensor similar to numpy.reshape. The output tensor has the same data as the input tensor but with a new shape.
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: shape, an 1-D NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64 shape tensor which specifies the new shape, At most one dimension of the new shape can be -1. In this case, the value is inferred from the size of the tensor and the remaining dimensions. a dimension could also be 0, in which case the actual dimension value is unchanged.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with a new shape, and its type and data is same as input.
NNADAPTER_RESIZE_NEAREST
Resizes the input tensor using the nearest interpolation.
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor with shape [N, C, …].
1: shape, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64 tensor, indicates the target shape of output exclude dim_N and dim_C.
2: scales, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32 tensor, indicates the scale of the output’s shape exclude dim_N and dim_C.
3: align_corners, a NNADAPTER_BOOL scalar. If True, the centers of the 4 corner pixels of the input and output tensors are aligned, preserving the values at the corner pixels.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same type as input.
NNADAPTER_RESIZE_LINEAR
Resizes the input tensor using the linear interpolation.
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor with shape [N, C, …].
1: shape, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64 tensor, indicates the target shape of output exclude dim_N and dim_C.
2: scales, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32 tensor, indicates the scale of the output’s shape exclude dim_N and dim_C.
3: align_corners, NNADAPTER_BOOL scalar. If True, the centers of the 4 corner pixels of the input and output tensors are aligned, preserving the values at the corner pixels.
4: align_mode, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, optional for linear interpolation. It can be ‘0’ for src_idx = scale_factor * (dst_indx + 0.5) - 0.5, can be ‘1’ for src_idx = scale_factor * dst_index.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same type as input.
NNADAPTER_SHAPE
Outputs an 1D tensor containing the shape of the input tensor.
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 tensor.
1: dtype, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, the value of NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64, specifies the dtype of the result.
Outputs:
0: output, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 tensor.
NNADAPTER_SIGMOID
Applies sigmoid activation to the input tensor element-wise. The output is calculated using this formula: output = 1 / (1 + exp(-input)).
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same shape and type as input.
NNADAPTER_SLICE
This operator produces a slice of input along multiple axes. Similar to numpy: https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/arrays.indexing.html Slice uses
axes,starts,endsandstepsto specify the start and end dimension and step for each axis in the list of axes, it uses this information to slice the input data tensor. If a negative value is passed to starts or ends such as −i, it represents the reverse position of the axis i−1 (here 0 is the initial position). If the value passed to starts or ends is greater than n (the number of elements in this dimension), it represents n. For slicing to the end of a dimension with unknown size, it is recommended to pass in INT_MAX. The size of axes must be equal to starts and ends.Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: axes, An optional NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 tensor that
startsandendsapply to, will be treated as [0, 1, …, len(starts) - 1] if it is empty.2: starts, starts indices of corresponding axis in
axes, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 tensor.3: ends, ends indices of corresponding axis in
axes, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 tensor.4: steps, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 1-D tensor, 1-D tensor of slice step of corresponding axis in
axes. Negative value means slicing backward.stepscannot be 0. Defaults to 1.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same shape and type as input.
NNADAPTER_SOFTMAX
Computes the normalized exponential values for the input tensor element-wise. The output is calculated using this formula: output = exp(input) / reduce_sum(exp(input), axis=axis, keepdims=true).
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: axis, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar. Defaults to 1. It represents the dimension along which softmax will be performed. It should be in range [-R, R), where R is the rank of input, negative value works the same way as axis+R.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same shape and type as input.
NNADAPTER_SPLIT
Split a tensor into a list of tensors along the specified axis.
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: axis, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar. It represents the dimension along which axis to split. It should be in range [-R, R), where R is the rank of input, negative value works the same way as axis+R.
2: split, An 1-D NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 tensor, each of values indicates the length of each output. Sum of the values must be equal to the dimension at
axisspecified.
Outputs:
0 ~ n-1: output0 ~ outputn-1, the results with the same type as the input.
NNADAPTER_SQUEEZE
Returns a tensor with all the dimensions of input of size 1 removed.
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: axes, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 tensor, indicates the dimensions to be squeezed, default to None. It should be in range [-R, R), where R is the rank of input, negative value works the same way as axis+R.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same type as input.
NNADAPTER_STACK
Concatenates a sequence of tensors into a single tensor along the specified axis. All input tensors must have the same shape.
Inputs:
0 ~ n-1: input0 ~ inputn-1, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
n: axis, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar. It represents the dimension along which axis to concatenate. It should be in range [-R-1, R+1), where R is the rank of input, negative value works the same way as axis+R+1.
Outputs:
0: output, the result with the same type as the inputs.
NNADAPTER_SUB
Performs element-wise binary subtraction(with Numpy-style broadcasting https://numpy.org/doc/stable/user/basics.broadcasting.html).
Inputs:
0: input0, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: input1, a tensor with the same type as input0.
2: fuse_code, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, specifies the activation to the result, must be one of NNAdapterFuseCode values.
Outputs:
0: output, the result with the same type as two inputs.
NNADAPTER_SWISH
Applies the Swish activation to the input tensor element-wise. The output is calculated using this formula: output = input / (1 + e ^ (-input)).
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same shape and type as input.
NNADAPTER_TANH
Applies the hyperbolic tangent activation to the input tensor element-wise. The output is calculated using this formula: output = tanh(input).
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same shape and type as input.
NNADAPTER_TOP_K
Retrieve the top-K largest elements along a specified axis.
Inputs:
input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: k, a NNADAPTER_INT32 or NNADAPTER_INT64 tensor, the number of top elements to look for along the axis.
2: axis, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, represents the dimension along which top_k will be performed. It should be in range [-R, R), where R is the rank of input, negative value works the same way as axis+R.
3: largest, a NNADAPTER_BOOL8 scalar, whether to return the top-K largest or smallest elements.
4: sorted, a NNADAPTER_BOOL8 scalar, whether to return the elements in sorted order.
5: return_indices_dtype, a NNADAPTER_INT32 scalar, the value of NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64, specifies the dtype of the indices.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same shape and type as input, top K values from the input tensor.
1: indices, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 or NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT64 tensor, the corresponding input tensor indices for the top K values.
NNADAPTER_TRANSPOSE
Transposes the input according to the perm, similar to numpy.transpose https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.transpose.html. For example, the input with shape (1, 2, 3) and perm=(1, 0, 2), the shape of output will be (2, 1, 3).
Inputs:
0: input0, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: perm, An optional 1-D NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 tensor, reverse the dimensions of input if perm is not given, otherwise permute the axes according to the values given.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same type as input.
NNADAPTER_UNSQUEEZE
Inserts a dimension of size 1 at the specified axis of the dimensions of input.
Inputs:
0: input, a NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT16, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_FLOAT32, NNADAPTER_TENSOR_QUANT_INT8_SYMM_PER_LAYER tensor.
1: axes, A NNADAPTER_TENSOR_INT32 tensor, indicates the dimensions to be inserted. It should be in range [-R, R), where R is the rank of input, negative value works the same way as axis+R+1.
Outputs:
0: output, a tensor with the same shape and type as input.