Reduce
Description
Perform reduction operations on the highest dimension according to the calculation rules defined in ReduceOp. For example, the input is x[N, H, W, C], the value of axis is 0, after the reduction is out[1, H, W, C], here is take ReduceSum as an example to introduce.
ReduceOp Definition
template <typename Tx, typename Ty = Tx>
struct IdentityFunctor {
HOSTDEVICE explicit inline IdentityFunctor(int n) {}
HOSTDEVICE inline Ty operator()(const Tx& x) const {
return static_cast<Ty>(x);
}
};
template <typename Tx, typename Ty = Tx>
struct AddFunctor {
inline Ty initial() { return static_cast<Ty>(0.0f); }
__device__ __forceinline__ Ty operator()(const Ty &a, const Ty &b) const {
return b + a;
}
};
Kernel Description
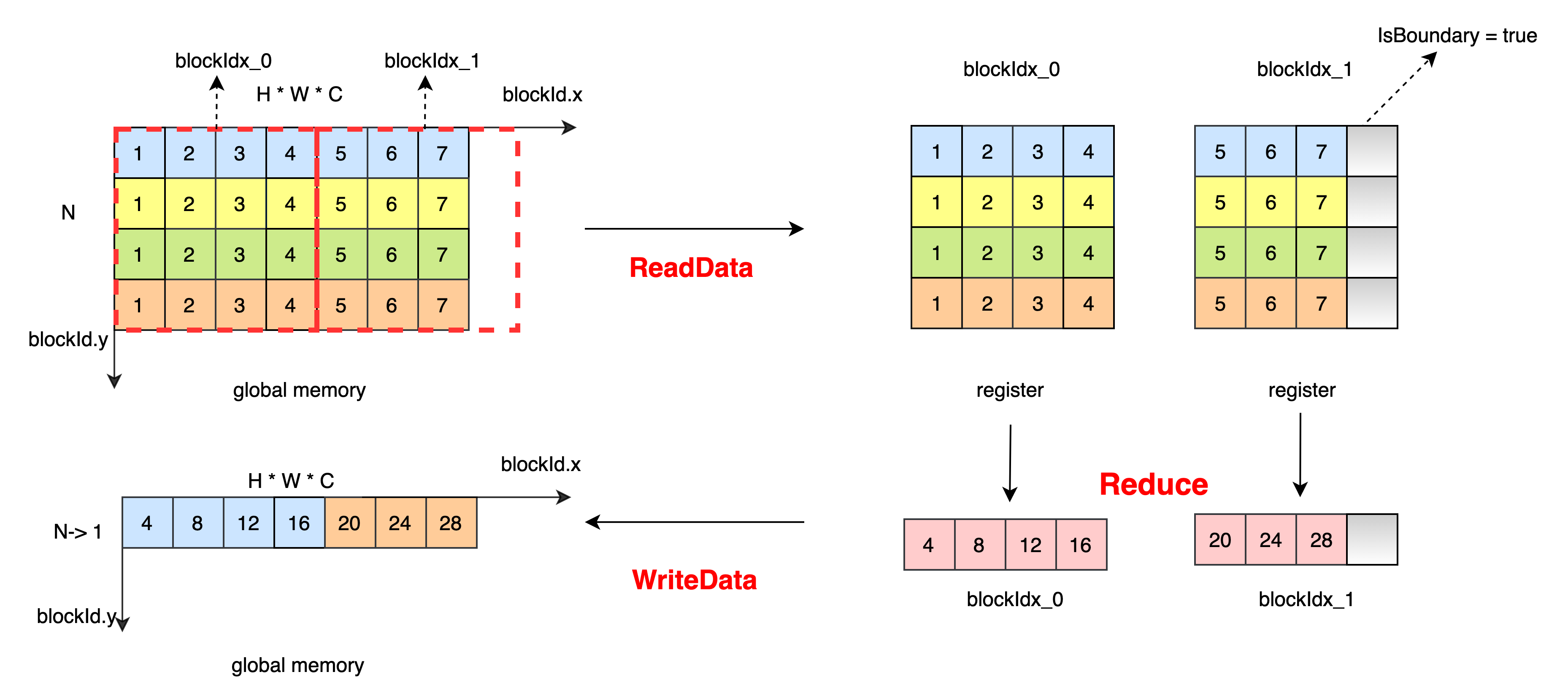
Perform reduction operations on the highest dimension, merge the dimensions that do not need to be reduced, and divide H * W * C into blocks according to NX and blockDim.x. For blockIdx_1, if the number of data is less than blockDim.x * NX, set IsBoundary = true to avoid memory fetching out of bounds. Read data from global memory to registers, each thread reads 4 elements, there is no dependence on data between threads, and the final result is obtained by intra-thread protocol operation. Write data from the register to the global memory.
The data processing process of ReduceSum is as follows:
Code
template <typename Tx, typename Ty, typename MPType, typename ReduceOp, typename TransformOp, bool IsBoundary = false>
__device__ void HigherDimImpl(const Tx* x, Ty* y, ReduceOp reducer,
TransformOp transform, MPType init,
int reduce_num, int left_num,
int block_num) {
const int NY = 2;
int idx = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x;
int idy = blockIdx.y * block_num; // block_offset of rows
Tx reduce_input[NY];
MPType reduce_compute[NY];
MPType result = init;
int block_offset = idy * left_num + idx + blockIdx.z * reduce_num * left_num; // the offset of this block
int store_offset = blockIdx.y * left_num + blockIdx.z * gridDim.y * left_num + idx;
const Tx* input = x + block_offset;
// how many columns left
int num = left_num - idx;
// how many rows have to be reduced
int loop = reduce_num - idy;
loop = loop > block_num ? block_size : loop;
for (int loop_index = 0; loop_index < loop; loop_index += NY) {
kps::ReadData<Tx, Tx, 1, NY, 1, IsBoundary>(&reduce_input[0], input + loop_index * left_num, num, NY, 1, left_num);
kps::ElementwiseUnary<Tx, MPType, REDUCE_VEC_num, 1, 1, TransformOp>(&reduce_compute[0], &reduce_input[0], transform);
kps::Reduce<MPType, NY, 1, 1, ReduceOp, kps::details::ReduceMode::kLocalMode>( &result, &reduce_compute[0], reducer, false);
}
Ty temp_data = static_cast<Ty>(result);
kps::WriteData<Ty, 1, 1, 1, IsBoundary>(y + store_offset, &temp_data, num);
}
template <typename Tx, typename Ty, typename MPType, typename ReduceOp, typename TransformOp>
__global__ void ReduceHigherDimKernel(const Tx* x, Ty* y, ReduceOp reducer,
TransformOp transform, MPType init,
int reduce_num, int left_num,
int blocking_num) {
// get the remaining data of this kernel
int num = left_num - blockIdx.x * blockDim.x;
if (num >= blockDim.x) {
// The remaining data is larger than blockdim.x
HigherDimImpl<Tx, Ty, MPType, AddFunctor<Tx, Ty>, IdentityFunctor<Tx, Ty>, false>(
x, y, AddFunctor<Tx, Ty>(), IdentityFunctor<Tx, Ty>(), init, reduce_num, left_num, blocking_num);
} else {
// The remaining data is smaller than blockdim.x, IsBounary must be true
HigherDimImpl<Tx, Ty, MPType, AddFunctor<Tx, Ty>, IdentityFunctor<Tx, Ty>, true>(
x, y, AddFunctor<Tx, Ty>(), IdentityFunctor<Tx, Ty>(), init, reduce_num, left_num, blocking_num);
}
}