

在飞桨黑客松比赛的第三期,飞桨社区核心开发者李健铭参与了CINN算子开发方向的任务。

 任务介绍
任务介绍
 设计文档
设计文档
 算子介绍
算子介绍
One-Hot算子(在本项目中,该算子函数名为OneHot,后文将统一称为OneHot)接受5个参数,输出1个张量。算子的参数含义如下。
indices索引张量。
on_value索引位置填充的值。
off_value非索引位置填充的值。
axis填充的轴。
OneHot(
indices=[0, 2, 2],
on_value=1,
off_value=0,
depth=4,
axis=0,
dtype=
"float32"
)
#
[[1. 0. 0]
# [0. 0. 1]
# [0. 0. 1]
# [0. 0. 0]]
OneHot(
indices=[
0,
2,
2],
on_value=
1,
off_value=
0,
depth=
4,
axis=
-1,
dtype=
"float32"
)
代码输出
#
[[1. 0. 0. 0.]
# [0. 0. 1. 0.]
# [0. 0. 1. 0.]]

CINN的结构比较复杂,我刚开始有些无从下手。为了明确任务的工作内容,我先学习了CINN已有的基础算子内容,分析算子开发的共性特征。
新增一个算子主要的工作可分为前端和后端两个部分,例如我们增加一个名为op的算子,需要完成以下的工作。
前端部分(cinn/frontend)
后端部分(cinn/hlir/op/contrib)
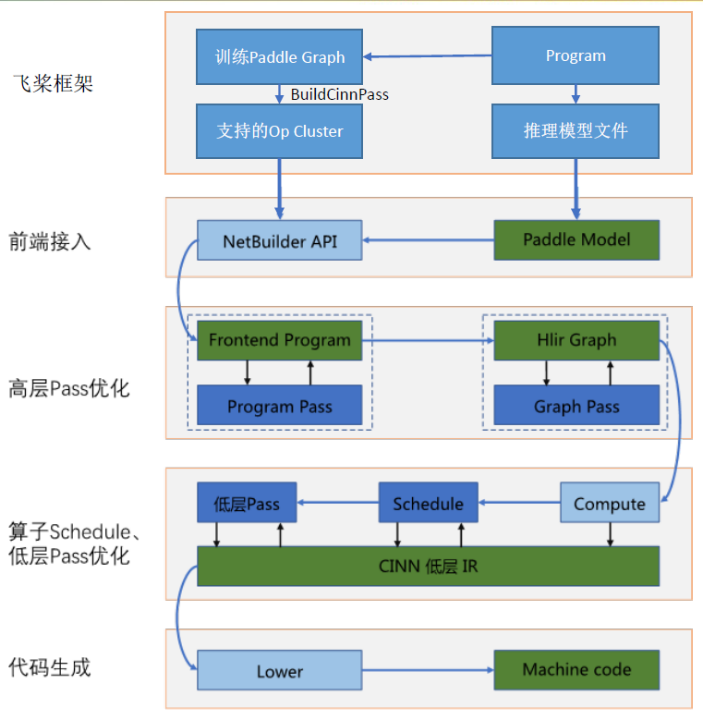
开发的重点是使用CINN IR构造算子的compute,其它内容可以参考CINN中已实现的算子,照葫芦画瓢。CINN IR是CINN底层进行计算表达的IR(Intermediate Representation),在框架中扮演重要角色。其中,Expr是 CINN IR的主要数据类型,它可以表示数值和计算。
下面是一些Expr的使用例子。这些例子包含了实现OneHot算子所涉及的全部CINN IR形式,目前我们了解这些就足够了。
// a+b
Expr a(
1);
Expr b(
1);
Expr c = a + b;
// int类型转换为float类型
Expr d = Cast::Make(common::Str2Type(
"float32"), a);
// 判断a与b是否相等
Expr e = EQ::Make(a, b)
// ?:三元表达式
Expr f = Select::Make(e, a, b)
https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/course/introduce/26351?directly=1&shared=1
注:课节10:深度学习编译器算子应用与开发介绍,推荐学习一下。
 代码开发
代码开发
在开始代码开发之前,我们需要先阅读CINN项目贡献指南 。文中介绍了开发环境和PR提交过程。搭建好开发环境,就可以开始编写代码了。
CINN项目贡献指南
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/CINN/pull/810
新增OneHot算子需要完成以下的工作。
前端部分(cinn/frontend)
后端部分(cinn/hlir/op/contrib)
 算子后端
算子后端
InferDtypeForOneHot
if (attrs.find(
"dtype") != attrs.
end()) {
dtype = absl::get<std::string>(attrs.at(
"dtype"));
}
InferShapeForOneHot
生成输出张量的过程是一个升维的过程,如果输入张量的shape是 (a, b),参数axis是0,则输出张量的shape为 (depth, a, b)。
在函数实现中,我们将depth插入输入张量的shape的axis轴,得到新的shape。
for (
int i =
0; i < ndim +
1; ++i) {
if (i == true_axis) {
new_shape.push_back(depth);
}
else {
new_shape.push_back(in_shape[indices_index++]);
}
}
OneHot
Tensor res = lang::Compute(
new_shape,
[=](
const
std::
vector<Expr>& iter) {
std::
vector<Expr> indices_indices;
for (
size_t i =
0; i < iter.size(); i++) {
if (
static_cast<
int>(i) == true_axis) {
continue;
}
indices_indices.push_back(iter[i]);
}
Expr idx = iter[true_axis];
Expr elem = ir::Cast::Make(idx.type(), indices(indices_indices));
return ir::Select::Make(ir::EQ::Make(elem, idx), on_value_cast, off_value_cast);
},
common::UniqName(output_name));
StrategyForOneHot
StrategyForOneHot函数整合算子的compute和schedule。这里schedule的内容与其它算子的保持相同即可。
std::shared_ptr
<framework::OpStrategy> StrategyForOneHot( … ){
...
//compute
framework::CINNCompute one
_hot_compute([
=](
lang::Args args, lang::RetValue* ret) {
//调用OneHot
ir::Tensor out = OneHot(indices, on
_value, off_value, depth, axis, common::Str2Type(dtype), tensor_name);
...
});
//schedule
framework::CINNSchedule one
_hot_schedule([
=](
lang::Args args, lang::RetValue* ret) {
//与其它算子相同
...
});
//整合算子的 compute 和 schedule
auto strategy = std::make_shared
<framework::OpStrategy>();
strategy->AddImpl(one
_hot_compute, one
_hot_schedule, "strategy.one_hot.x86", 1);
return strategy;
}
算子注册
使用CINN_REGISTER_HELPER宏注册算子,设置好算子的参数数量、参数名称和相关的函数名等。
CINN_REGISTER_HELPER(one_hot_ops) {
CINN_REGISTER_OP(one_hot)
.describe(
"Returns a one-hot tensor where the locations repsented by indices take value `on_value`, "
"other locations take value `off_value`.")
.set_num_inputs(
3)
.set_num_outputs(
1)
.set_attr<cinn::hlir::framework::StrategyFunction>(
"CINNStrategy", cinn::hlir::op::StrategyForOneHot)
.set_attr(
"infershape", MakeOpFunction(cinn::hlir::op::InferShapeForOneHot))
.set_attr(
"inferdtype", MakeOpFunction(cinn::hlir::op::InferDtypeForOneHot))
.set_support_level(
4);
return
true;
}
}
最后在cinn/hlir/op/use_ops.h中注册算子,后端的内容就完成了。
CINN_USE_REGISTER(one_hot_ops)
 算子前端
算子前端
前端的工作比较简单,主要是在NetBuilder中实现OneHot的前端接口,函数实现有固定的形式。
Variable NetBuilder::OneHot( … ) {
return CustomInstr(
"one_hot", {indices, on_value, off_value}, {{"depth", depth}, {"axis", axis}, {"dtype", dtype}}).front();
}
 算子单测
算子单测
完成新算子的代码开发后,必须编写新算子的单测。算子的前端和后端均需要测试。在前端,我们测试算子的计算结果的正确性。在后端,我们测试算子代码生成的结果的正确性。单测的内容比较模式化,我们可以模仿其它算子的单测进行编写,
详细代码可查看PR
编译完成后,使用ctest指令运行单测。
ctest -R one_hot_test
ctest -R net_builder_test
 总结
总结
在飞桨黑客松比赛的第三期,飞桨社区核心开发者李健铭参与了CINN算子开发方向的任务。

 任务介绍
任务介绍
 设计文档
设计文档
 算子介绍
算子介绍
One-Hot算子(在本项目中,该算子函数名为OneHot,后文将统一称为OneHot)接受5个参数,输出1个张量。算子的参数含义如下。
indices索引张量。
on_value索引位置填充的值。
off_value非索引位置填充的值。
axis填充的轴。
OneHot(
indices=[0, 2, 2],
on_value=1,
off_value=0,
depth=4,
axis=0,
dtype=
"float32"
)
#
[[1. 0. 0]
# [0. 0. 1]
# [0. 0. 1]
# [0. 0. 0]]
OneHot(
indices=[
0,
2,
2],
on_value=
1,
off_value=
0,
depth=
4,
axis=
-1,
dtype=
"float32"
)
代码输出
#
[[1. 0. 0. 0.]
# [0. 0. 1. 0.]
# [0. 0. 1. 0.]]

CINN的结构比较复杂,我刚开始有些无从下手。为了明确任务的工作内容,我先学习了CINN已有的基础算子内容,分析算子开发的共性特征。
新增一个算子主要的工作可分为前端和后端两个部分,例如我们增加一个名为op的算子,需要完成以下的工作。
前端部分(cinn/frontend)
后端部分(cinn/hlir/op/contrib)

开发的重点是使用CINN IR构造算子的compute,其它内容可以参考CINN中已实现的算子,照葫芦画瓢。CINN IR是CINN底层进行计算表达的IR(Intermediate Representation),在框架中扮演重要角色。其中,Expr是 CINN IR的主要数据类型,它可以表示数值和计算。
下面是一些Expr的使用例子。这些例子包含了实现OneHot算子所涉及的全部CINN IR形式,目前我们了解这些就足够了。
// a+b
Expr a(
1);
Expr b(
1);
Expr c = a + b;
// int类型转换为float类型
Expr d = Cast::Make(common::Str2Type(
"float32"), a);
// 判断a与b是否相等
Expr e = EQ::Make(a, b)
// ?:三元表达式
Expr f = Select::Make(e, a, b)
https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/course/introduce/26351?directly=1&shared=1
注:课节10:深度学习编译器算子应用与开发介绍,推荐学习一下。
 代码开发
代码开发
在开始代码开发之前,我们需要先阅读CINN项目贡献指南 。文中介绍了开发环境和PR提交过程。搭建好开发环境,就可以开始编写代码了。
CINN项目贡献指南
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/CINN/pull/810
新增OneHot算子需要完成以下的工作。
前端部分(cinn/frontend)
后端部分(cinn/hlir/op/contrib)
 算子后端
算子后端
InferDtypeForOneHot
if (attrs.find(
"dtype") != attrs.
end()) {
dtype = absl::get<std::string>(attrs.at(
"dtype"));
}
InferShapeForOneHot
生成输出张量的过程是一个升维的过程,如果输入张量的shape是 (a, b),参数axis是0,则输出张量的shape为 (depth, a, b)。
在函数实现中,我们将depth插入输入张量的shape的axis轴,得到新的shape。
for (
int i =
0; i < ndim +
1; ++i) {
if (i == true_axis) {
new_shape.push_back(depth);
}
else {
new_shape.push_back(in_shape[indices_index++]);
}
}
OneHot
Tensor res = lang::Compute(
new_shape,
[=](
const
std::
vector<Expr>& iter) {
std::
vector<Expr> indices_indices;
for (
size_t i =
0; i < iter.size(); i++) {
if (
static_cast<
int>(i) == true_axis) {
continue;
}
indices_indices.push_back(iter[i]);
}
Expr idx = iter[true_axis];
Expr elem = ir::Cast::Make(idx.type(), indices(indices_indices));
return ir::Select::Make(ir::EQ::Make(elem, idx), on_value_cast, off_value_cast);
},
common::UniqName(output_name));
StrategyForOneHot
StrategyForOneHot函数整合算子的compute和schedule。这里schedule的内容与其它算子的保持相同即可。
std::shared_ptr
<framework::OpStrategy> StrategyForOneHot( … ){
...
//compute
framework::CINNCompute one
_hot_compute([
=](
lang::Args args, lang::RetValue* ret) {
//调用OneHot
ir::Tensor out = OneHot(indices, on
_value, off_value, depth, axis, common::Str2Type(dtype), tensor_name);
...
});
//schedule
framework::CINNSchedule one
_hot_schedule([
=](
lang::Args args, lang::RetValue* ret) {
//与其它算子相同
...
});
//整合算子的 compute 和 schedule
auto strategy = std::make_shared
<framework::OpStrategy>();
strategy->AddImpl(one
_hot_compute, one
_hot_schedule, "strategy.one_hot.x86", 1);
return strategy;
}
算子注册
使用CINN_REGISTER_HELPER宏注册算子,设置好算子的参数数量、参数名称和相关的函数名等。
CINN_REGISTER_HELPER(one_hot_ops) {
CINN_REGISTER_OP(one_hot)
.describe(
"Returns a one-hot tensor where the locations repsented by indices take value `on_value`, "
"other locations take value `off_value`.")
.set_num_inputs(
3)
.set_num_outputs(
1)
.set_attr<cinn::hlir::framework::StrategyFunction>(
"CINNStrategy", cinn::hlir::op::StrategyForOneHot)
.set_attr(
"infershape", MakeOpFunction(cinn::hlir::op::InferShapeForOneHot))
.set_attr(
"inferdtype", MakeOpFunction(cinn::hlir::op::InferDtypeForOneHot))
.set_support_level(
4);
return
true;
}
}
最后在cinn/hlir/op/use_ops.h中注册算子,后端的内容就完成了。
CINN_USE_REGISTER(one_hot_ops)
 算子前端
算子前端
前端的工作比较简单,主要是在NetBuilder中实现OneHot的前端接口,函数实现有固定的形式。
Variable NetBuilder::OneHot( … ) {
return CustomInstr(
"one_hot", {indices, on_value, off_value}, {{"depth", depth}, {"axis", axis}, {"dtype", dtype}}).front();
}
 算子单测
算子单测
完成新算子的代码开发后,必须编写新算子的单测。算子的前端和后端均需要测试。在前端,我们测试算子的计算结果的正确性。在后端,我们测试算子代码生成的结果的正确性。单测的内容比较模式化,我们可以模仿其它算子的单测进行编写,
详细代码可查看PR
编译完成后,使用ctest指令运行单测。
ctest -R one_hot_test
ctest -R net_builder_test
 总结
总结