

文本搜索
预训练语言模型
Dual encoder架构使用两个BERT模型,query model和context model分别将问题和对应的待查找文本映射到768维的语义空间。为保证在实际检索过程中的准确度,该模型的训练策略为:尽可能的使问题与对应的文本间的距离接近,而与无关的文本间的距离拉远。Cross encoder则使用一个BERT模型同时对问题和文本进行编码。
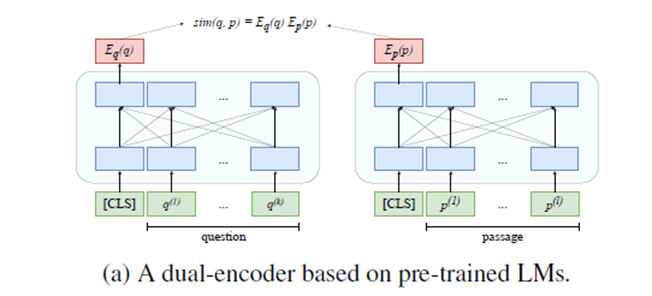
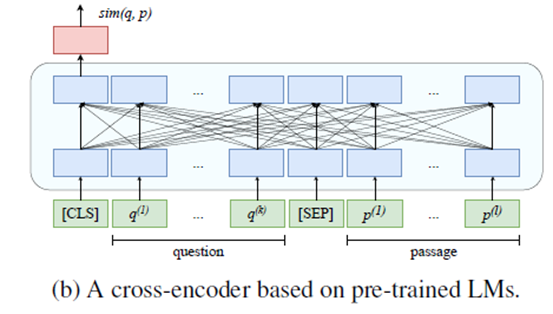
RocketQA为百度对DPR(Dense Passage Retrieval)的训练策略进行优化和改进得到的模型。一般的训练策略为:对于给定问题文本,使其在空间中的表示尽可能靠近正样本同时远离负样本。In batch negatives训练策略则将同一批次内除当前问题的正样本之外的其他样本均视为负样本(包括当前问题的负样本,和其它问题的正、负样本)。相比于在同一批次内进行采样,RocketQA基于飞桨的分布式训练能力,使用了跨批次的负采样策略。实验证明,适当增大batch size可以较好的提升模型的性能。除此之外,考虑到在实际应用中,训练数据存在漏标、错标等情况,准确率不高。为尽可能降低假负例对模型效果的影响,RocketQA使用cross model对文本进行打分,借此来筛去部分不符合要求的标注数据。同时,RocketQA也通过使用交互模型来得到更多相关的弱监督数据帮助其训练。
戳官方Repo了解RocketQA详情:
系统架构工具
JINA提供了一整套搭建搜索系统的开源工具,其主要产品为Document,Executor和Flow。Document为基础数据结构,Executor负责对Document进行处理,Flow则负责搭建整个工作流程。
项目实现
本文使用百度飞桨框架和RocketQA模型,基于JINA全家桶构建了含有Retrieve、Rerank两个阶段的文本召回系统。接下来将详述项目实现过程。
文本问答的主要流程为:召回(retriever),重排(reranker)和阅读理解(reader)。在召回阶段,本项目使用RocketQA(Dual model)将问题文本映射为向量的形式,之后,近似最近邻搜索系统会在已有的索引库中搜索与之距离最近的top-k向量,并返回符合阈值条件的候选向量;在重排阶段,则会使用RocketQA的Cross model对所有召回向量进行打分,最后根据排序返回最终得分前三的文本。
class RocketqaDeExecutor(Executor):
def __init__(self,model_name="zh_dureader_de",use_Cuda=True,device_Id=0,batch_Size=32,*args,**kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.model = rocketqa.load_model(model=model_name,use_cuda=True,device_id=device_Id,batch_size=batch_Size)
@requests(on="/index")
def encode_passage(self,docs:DocumentArray,**kwargs):
embeddings = self.model.encode_para(para=docs.texts)
docs.embeddings = [embedding for embedding in embeddings]
@requests(on="/search")
def encode_query(self,docs,**kwargs):
print("retriever is working......")
start = time.time()
for doc in docs:
generator_temp = self.model.encode_query(query=[doc.text])
for temp in generator_temp:
doc.embedding = temp
end = time.time()
print("retrieve time: ",end-start,"s")
使用RocketqaCe模型来实现第二阶段的打分重排。在”/search”阶段,该Executor将前一步处理后得到嵌入文本向量与问题向量一起处理,得到每条召回结果的分数,并根据分数具体排名。在”/index”阶段,该Executor不参与工作。
class RocketqaCeExecutor(Executor):
def __init__(self,model_Name="zh_dureader_ce",use_Cuda=True,device_Id=0,batch_Size=32,*args,**kwargs):
super().__init__(*args,**kwargs)
self.model = rocketqa.load_model(model=model_Name,use_cuda=True,device_id=device_Id,batch_size=batch_Size)
@requests(on="/search")
def rerank(self,docs,**kwargs):
print("reranker is working......")
print("召回结果排序中......")
start = time.time()
for doc in docs:
str_list = []
for m in doc.matches:
str_list.append(m.text)
doc.matches = []
scores = []
score_generator = self.model.matching(query=[doc.text]*len(str_list),para=str_list)
for g in score_generator:
scores.append(g)
scores = np.array(scores).argsort()
doc.matches.append(Document(text=str_list[scores[-1]]))
doc.matches.append(Document(text=str_list[scores[-2]]))
doc.matches.append(Document(text=str_list[scores[-3]]))
end = time.time()
print("rerank time:",end-start,"s")def main(order):
if order == 'index':
if Path('./workspace').exists():
print('./workspace exists, please deleted it if you want to reindexi')
return 0
data_path = sys.argv[2]
if data_path is None:
print("No data_path!")
index(data_path)
elif order == 'query':
query()
def index(path):
with test_flow:
test_flow.index(inputs=read_file(path), show_progress=True)
def query():
with test_flow:
while(True):
query = input("请输入查询选项:")
if query == "exit":
break
query = Document(text=query)
docs = test_flow.search(inputs=query)
matches = docs[0].matches
print("搜索答案为:")
ids = 1
for match in matches:
print("推荐答案排行,NO.",ids)
print(match.text)
ids = ids + 1效果展示
运行python wow.py index data_path来建立索引库:
运行python wow.py query来执行搜索:

总结
此外,飞桨自然语言处理模型库PaddleNLP也基于RocketQA等前沿模型搭建了完整的检索系统、问答系统,亲测好用。传送门:
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/tree/develop/applications/experimental/pipelines
戳GitHub主页与我交流:https://github.com/Elvisambition

关注【飞桨PaddlePaddle】公众号
获取更多技术内容~
文本搜索
预训练语言模型
Dual encoder架构使用两个BERT模型,query model和context model分别将问题和对应的待查找文本映射到768维的语义空间。为保证在实际检索过程中的准确度,该模型的训练策略为:尽可能的使问题与对应的文本间的距离接近,而与无关的文本间的距离拉远。Cross encoder则使用一个BERT模型同时对问题和文本进行编码。


RocketQA为百度对DPR(Dense Passage Retrieval)的训练策略进行优化和改进得到的模型。一般的训练策略为:对于给定问题文本,使其在空间中的表示尽可能靠近正样本同时远离负样本。In batch negatives训练策略则将同一批次内除当前问题的正样本之外的其他样本均视为负样本(包括当前问题的负样本,和其它问题的正、负样本)。相比于在同一批次内进行采样,RocketQA基于飞桨的分布式训练能力,使用了跨批次的负采样策略。实验证明,适当增大batch size可以较好的提升模型的性能。除此之外,考虑到在实际应用中,训练数据存在漏标、错标等情况,准确率不高。为尽可能降低假负例对模型效果的影响,RocketQA使用cross model对文本进行打分,借此来筛去部分不符合要求的标注数据。同时,RocketQA也通过使用交互模型来得到更多相关的弱监督数据帮助其训练。
戳官方Repo了解RocketQA详情:
系统架构工具
JINA提供了一整套搭建搜索系统的开源工具,其主要产品为Document,Executor和Flow。Document为基础数据结构,Executor负责对Document进行处理,Flow则负责搭建整个工作流程。
项目实现
本文使用百度飞桨框架和RocketQA模型,基于JINA全家桶构建了含有Retrieve、Rerank两个阶段的文本召回系统。接下来将详述项目实现过程。
文本问答的主要流程为:召回(retriever),重排(reranker)和阅读理解(reader)。在召回阶段,本项目使用RocketQA(Dual model)将问题文本映射为向量的形式,之后,近似最近邻搜索系统会在已有的索引库中搜索与之距离最近的top-k向量,并返回符合阈值条件的候选向量;在重排阶段,则会使用RocketQA的Cross model对所有召回向量进行打分,最后根据排序返回最终得分前三的文本。
class RocketqaDeExecutor(Executor):
def __init__(self,model_name="zh_dureader_de",use_Cuda=True,device_Id=0,batch_Size=32,*args,**kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.model = rocketqa.load_model(model=model_name,use_cuda=True,device_id=device_Id,batch_size=batch_Size)
@requests(on="/index")
def encode_passage(self,docs:DocumentArray,**kwargs):
embeddings = self.model.encode_para(para=docs.texts)
docs.embeddings = [embedding for embedding in embeddings]
@requests(on="/search")
def encode_query(self,docs,**kwargs):
print("retriever is working......")
start = time.time()
for doc in docs:
generator_temp = self.model.encode_query(query=[doc.text])
for temp in generator_temp:
doc.embedding = temp
end = time.time()
print("retrieve time: ",end-start,"s")
使用RocketqaCe模型来实现第二阶段的打分重排。在”/search”阶段,该Executor将前一步处理后得到嵌入文本向量与问题向量一起处理,得到每条召回结果的分数,并根据分数具体排名。在”/index”阶段,该Executor不参与工作。
class RocketqaCeExecutor(Executor):
def __init__(self,model_Name="zh_dureader_ce",use_Cuda=True,device_Id=0,batch_Size=32,*args,**kwargs):
super().__init__(*args,**kwargs)
self.model = rocketqa.load_model(model=model_Name,use_cuda=True,device_id=device_Id,batch_size=batch_Size)
@requests(on="/search")
def rerank(self,docs,**kwargs):
print("reranker is working......")
print("召回结果排序中......")
start = time.time()
for doc in docs:
str_list = []
for m in doc.matches:
str_list.append(m.text)
doc.matches = []
scores = []
score_generator = self.model.matching(query=[doc.text]*len(str_list),para=str_list)
for g in score_generator:
scores.append(g)
scores = np.array(scores).argsort()
doc.matches.append(Document(text=str_list[scores[-1]]))
doc.matches.append(Document(text=str_list[scores[-2]]))
doc.matches.append(Document(text=str_list[scores[-3]]))
end = time.time()
print("rerank time:",end-start,"s")def main(order):
if order == 'index':
if Path('./workspace').exists():
print('./workspace exists, please deleted it if you want to reindexi')
return 0
data_path = sys.argv[2]
if data_path is None:
print("No data_path!")
index(data_path)
elif order == 'query':
query()
def index(path):
with test_flow:
test_flow.index(inputs=read_file(path), show_progress=True)
def query():
with test_flow:
while(True):
query = input("请输入查询选项:")
if query == "exit":
break
query = Document(text=query)
docs = test_flow.search(inputs=query)
matches = docs[0].matches
print("搜索答案为:")
ids = 1
for match in matches:
print("推荐答案排行,NO.",ids)
print(match.text)
ids = ids + 1效果展示
运行python wow.py index data_path来建立索引库:

运行python wow.py query来执行搜索:

总结
此外,飞桨自然语言处理模型库PaddleNLP也基于RocketQA等前沿模型搭建了完整的检索系统、问答系统,亲测好用。传送门:
https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/tree/develop/applications/experimental/pipelines
戳GitHub主页与我交流:https://github.com/Elvisambition

关注【飞桨PaddlePaddle】公众号
获取更多技术内容~